http://scholar.google.com/citations?hl=en&user=95SvbM8AAAAJ
P. M. Gautam, Chandkiram; Tiwary, Chandra Sekhar; Machado, Leonardo D.; Jose, Sujin; Ozden, Sehmus; Biradar, Santoshkumar; Galvao, Douglas S.; Sonker, Rakesh K.; Yadav, B. C.; Vajtai, Robert; Ajayan,
Synthesis and porous h-BN 3D architectures for effective humidity and gas sensors Authors Journal Article
Em: RSC Advances, vol. 6, não 91, pp. 87888-87896, 2016.
@article{Gautam2016,
title = {Synthesis and porous h-BN 3D architectures for effective humidity and gas sensors Authors},
author = {P. M. Gautam, Chandkiram and Tiwary, Chandra Sekhar and Machado, Leonardo D. and Jose, Sujin and Ozden, Sehmus and Biradar, Santoshkumar and Galvao, Douglas S. and Sonker, Rakesh K. and Yadav, B. C. and Vajtai, Robert and Ajayan},
url = {pubs.rsc.org/en/Content/ArticleHtml/2016/RA/c6ra18833h},
doi = {10.1039/C6RA18833H},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-09-09},
journal = {RSC Advances},
volume = {6},
number = {91},
pages = {87888-87896},
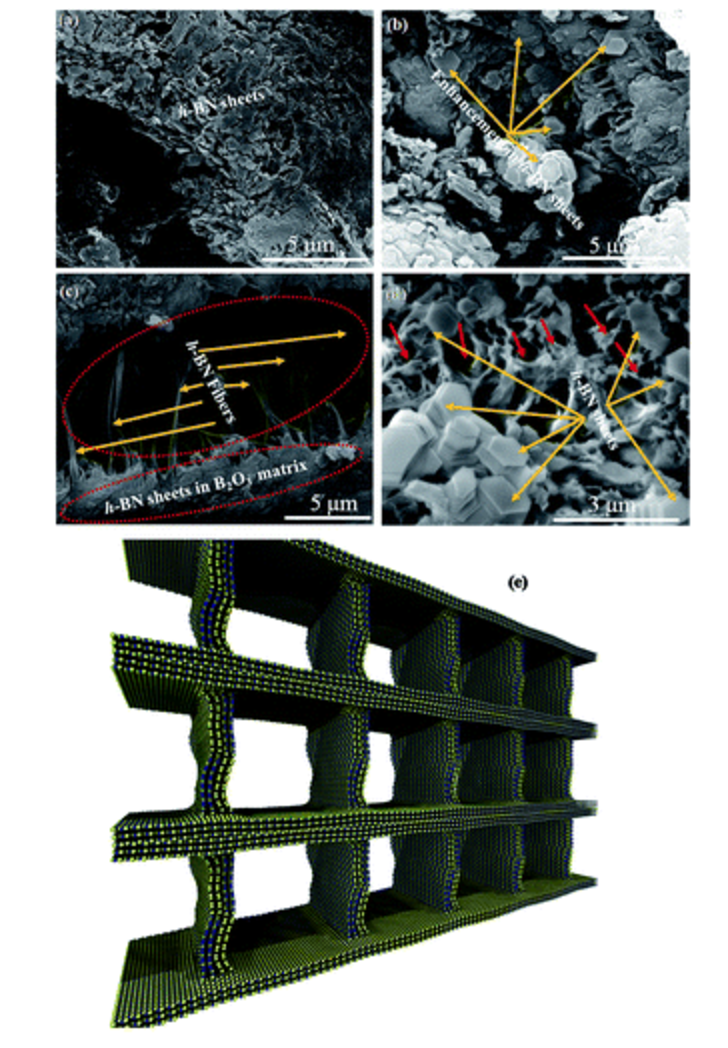
abstract = {3D (three dimensional) architectures synthesised using an easily scalable solid state method which results in an interconnected network of porous h-BN sheets with boron trioxide are reported in this study. The boron trioxide acts as a nucleating agent for the formation of laterally large nanosheets of h-BN with a low density and increases the specific surface area. The stable form shows improved mechanical properties (experimentally and using MD simulation) and serves as a suitable material for humidity and liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) sensor applications. The sensor shows stability for up to several months without losing its sensitivity.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Gaffo, Luciana; Couto Jr, Odilon DD; Giro, Ronaldo; Brasil, Maria JSP; Galvao, Douglas S; Cerdeira, Fernando; de Oliveira Jr, Osvaldo N; Wohnrath, Karen
Effects of chlorine gas exposure on the optical properties of rhodium phthalocyanine films Journal Article
Em: Solid state communications, vol. 131, não 1, pp. 53–56, 2004.
@article{gaffo2004effects,
title = {Effects of chlorine gas exposure on the optical properties of rhodium phthalocyanine films},
author = {Gaffo, Luciana and Couto Jr, Odilon DD and Giro, Ronaldo and Brasil, Maria JSP and Galvao, Douglas S and Cerdeira, Fernando and de Oliveira Jr, Osvaldo N and Wohnrath, Karen},
url = {http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0038109804002996},
year = {2004},
date = {2004-01-01},
journal = {Solid state communications},
volume = {131},
number = {1},
pages = {53--56},
publisher = {Pergamon},
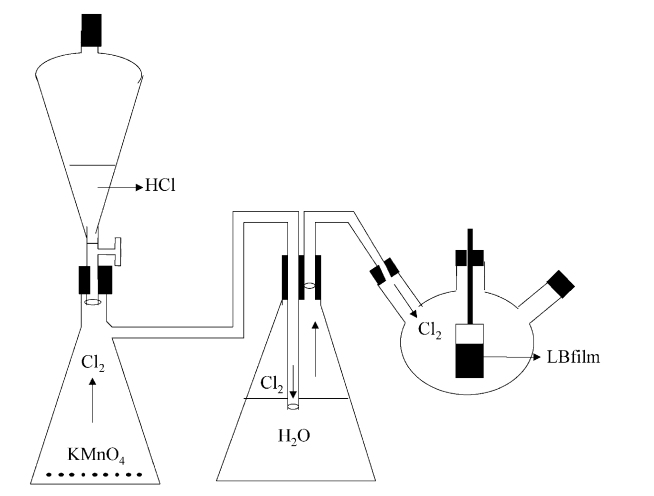
abstract = {We investigated the effects of exposing rhodium phthalocyanine films deposited on glass substrates by the Lagmuir–Blodgett technique to chlorine gas. The visual aspect of the films is altered upon chlorination, changing in color from blue to transparent. We performed optical absorption and Raman Scattering measurements on our films prior to and after exposing it to chlorine gas. We observed a pronounced quenching of the characteristic triplet centered around the Q-absorption band at 662 nm as a result of chlorine incorporation. Another absorption band, in the near UV part of the spectrum, is not greatly affected by the process. No new optical structures appear as a consequence of chlorination. Equivalent effects were observed in the Raman spectra. Leaving the previously exposed films in air for several hours results in a slow partial recovery of the optical spectra. This recovery, as well as the amount of original quenching, depends on the amount of time during which the film was exposed to chlorine.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Del Nero, J; Galvao, DS; Laks, B
Electronic structure investigation of biosensor polymer Journal Article
Em: Optical Materials, vol. 21, não 1, pp. 461–466, 2003.
@article{del2003electronic,
title = {Electronic structure investigation of biosensor polymer},
author = {Del Nero, J and Galvao, DS and Laks, B},
url = {http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925346702001830},
year = {2003},
date = {2003-01-01},
journal = {Optical Materials},
volume = {21},
number = {1},
pages = {461--466},
publisher = {Elsevier},
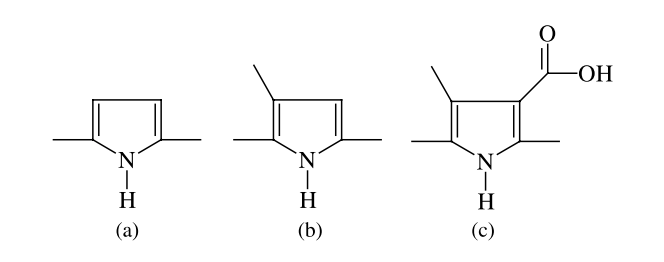
abstract = {We report a theoretical study of the ground, excited and ionic states of 3-methyl pyrrole-4-carboxilic acid (MPC) oligomers and related compounds which present conformational defects. Our results reveal the existence of differentiated electronic behavior for MPC with relation to oligopyrrole derivatives. These electronic features might explain why MPC works properly as a biosensor for cytochrome C while no voltametric response is observed for unsubstituted poly(pyrrole).},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2016
P. M. Gautam, Chandkiram; Tiwary, Chandra Sekhar; Machado, Leonardo D.; Jose, Sujin; Ozden, Sehmus; Biradar, Santoshkumar; Galvao, Douglas S.; Sonker, Rakesh K.; Yadav, B. C.; Vajtai, Robert; Ajayan,
Synthesis and porous h-BN 3D architectures for effective humidity and gas sensors Authors Journal Article
Em: RSC Advances, vol. 6, não 91, pp. 87888-87896, 2016.
Resumo | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Boron Nitride tubes, Modeling, Molecular Dynamics, Sensors
@article{Gautam2016,
title = {Synthesis and porous h-BN 3D architectures for effective humidity and gas sensors Authors},
author = {P. M. Gautam, Chandkiram and Tiwary, Chandra Sekhar and Machado, Leonardo D. and Jose, Sujin and Ozden, Sehmus and Biradar, Santoshkumar and Galvao, Douglas S. and Sonker, Rakesh K. and Yadav, B. C. and Vajtai, Robert and Ajayan},
url = {pubs.rsc.org/en/Content/ArticleHtml/2016/RA/c6ra18833h},
doi = {10.1039/C6RA18833H},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-09-09},
journal = {RSC Advances},
volume = {6},
number = {91},
pages = {87888-87896},
abstract = {3D (three dimensional) architectures synthesised using an easily scalable solid state method which results in an interconnected network of porous h-BN sheets with boron trioxide are reported in this study. The boron trioxide acts as a nucleating agent for the formation of laterally large nanosheets of h-BN with a low density and increases the specific surface area. The stable form shows improved mechanical properties (experimentally and using MD simulation) and serves as a suitable material for humidity and liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) sensor applications. The sensor shows stability for up to several months without losing its sensitivity.},
keywords = {Boron Nitride tubes, Modeling, Molecular Dynamics, Sensors},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2004
Gaffo, Luciana; Couto Jr, Odilon DD; Giro, Ronaldo; Brasil, Maria JSP; Galvao, Douglas S; Cerdeira, Fernando; de Oliveira Jr, Osvaldo N; Wohnrath, Karen
Effects of chlorine gas exposure on the optical properties of rhodium phthalocyanine films Journal Article
Em: Solid state communications, vol. 131, não 1, pp. 53–56, 2004.
Resumo | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Films, Phthalocyanine, Sensors
@article{gaffo2004effects,
title = {Effects of chlorine gas exposure on the optical properties of rhodium phthalocyanine films},
author = {Gaffo, Luciana and Couto Jr, Odilon DD and Giro, Ronaldo and Brasil, Maria JSP and Galvao, Douglas S and Cerdeira, Fernando and de Oliveira Jr, Osvaldo N and Wohnrath, Karen},
url = {http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0038109804002996},
year = {2004},
date = {2004-01-01},
journal = {Solid state communications},
volume = {131},
number = {1},
pages = {53--56},
publisher = {Pergamon},
abstract = {We investigated the effects of exposing rhodium phthalocyanine films deposited on glass substrates by the Lagmuir–Blodgett technique to chlorine gas. The visual aspect of the films is altered upon chlorination, changing in color from blue to transparent. We performed optical absorption and Raman Scattering measurements on our films prior to and after exposing it to chlorine gas. We observed a pronounced quenching of the characteristic triplet centered around the Q-absorption band at 662 nm as a result of chlorine incorporation. Another absorption band, in the near UV part of the spectrum, is not greatly affected by the process. No new optical structures appear as a consequence of chlorination. Equivalent effects were observed in the Raman spectra. Leaving the previously exposed films in air for several hours results in a slow partial recovery of the optical spectra. This recovery, as well as the amount of original quenching, depends on the amount of time during which the film was exposed to chlorine.},
keywords = {Films, Phthalocyanine, Sensors},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2003
Del Nero, J; Galvao, DS; Laks, B
Electronic structure investigation of biosensor polymer Journal Article
Em: Optical Materials, vol. 21, não 1, pp. 461–466, 2003.
Resumo | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Conducting Polymers, Electronic Structure, Sensors
@article{del2003electronic,
title = {Electronic structure investigation of biosensor polymer},
author = {Del Nero, J and Galvao, DS and Laks, B},
url = {http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925346702001830},
year = {2003},
date = {2003-01-01},
journal = {Optical Materials},
volume = {21},
number = {1},
pages = {461--466},
publisher = {Elsevier},
abstract = {We report a theoretical study of the ground, excited and ionic states of 3-methyl pyrrole-4-carboxilic acid (MPC) oligomers and related compounds which present conformational defects. Our results reveal the existence of differentiated electronic behavior for MPC with relation to oligopyrrole derivatives. These electronic features might explain why MPC works properly as a biosensor for cytochrome C while no voltametric response is observed for unsubstituted poly(pyrrole).},
keywords = {Conducting Polymers, Electronic Structure, Sensors},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}


