http://scholar.google.com/citations?hl=en&user=95SvbM8AAAAJ
1.
Galvao, Douglas Soares; Rodrigues, Varlei; Ugarte, Daniel; Legoas, Sergio Benites
The role of carbon contamination in metallic nanowires Journal Article
Em: Materials Research, vol. 7, não 2, pp. 339–342, 2004.
@article{galvao2004role,
title = {The role of carbon contamination in metallic nanowires},
author = {Galvao, Douglas Soares and Rodrigues, Varlei and Ugarte, Daniel and Legoas, Sergio Benites},
url = {http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?pid=S1516-14392004000200020&script=sci_arttext},
year = {2004},
date = {2004-01-01},
journal = {Materials Research},
volume = {7},
number = {2},
pages = {339--342},
publisher = {SciELO Brasil},
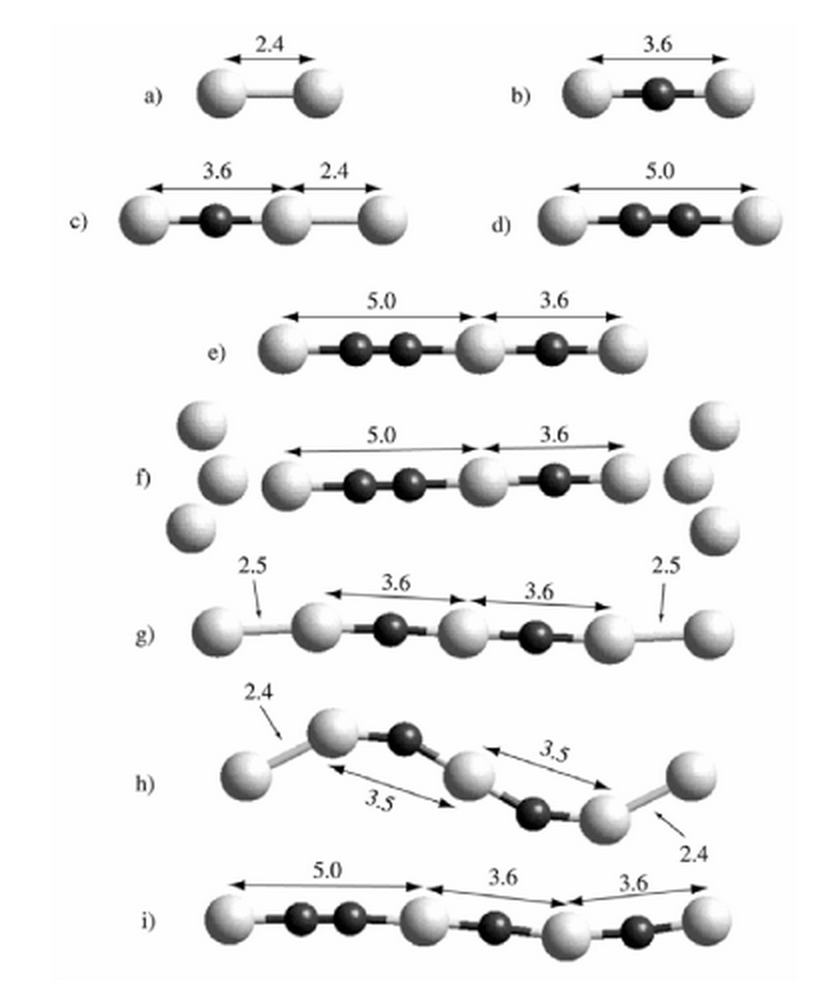
abstract = {Metallic nanowires have attracted much attention in the last years due to new phenomena such as quantum conductance and the existence of unexpected long interatomic distances attaining 0.3-0.5 nm. These large distances represented a challenge for physical interpretation. In this work we present experimental data from high-resolution transmission electron microscopy and results from ab initio calculations for suspended gold chains and show that these large distances can be easily explained by the presence of carbon atoms as contaminants. In principle the present conclusions can be also applied to other metallic nanowires (such as Ag and Pt) whose structures also present large interatomic distances.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Metallic nanowires have attracted much attention in the last years due to new phenomena such as quantum conductance and the existence of unexpected long interatomic distances attaining 0.3-0.5 nm. These large distances represented a challenge for physical interpretation. In this work we present experimental data from high-resolution transmission electron microscopy and results from ab initio calculations for suspended gold chains and show that these large distances can be easily explained by the presence of carbon atoms as contaminants. In principle the present conclusions can be also applied to other metallic nanowires (such as Ag and Pt) whose structures also present large interatomic distances.
2004
1.
Galvao, Douglas Soares; Rodrigues, Varlei; Ugarte, Daniel; Legoas, Sergio Benites
The role of carbon contamination in metallic nanowires Journal Article
Em: Materials Research, vol. 7, não 2, pp. 339–342, 2004.
Resumo | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Contaminantes, Electronic Structure, Linear Atomic Chains, Metallic Nanowires, Structure
@article{galvao2004role,
title = {The role of carbon contamination in metallic nanowires},
author = {Galvao, Douglas Soares and Rodrigues, Varlei and Ugarte, Daniel and Legoas, Sergio Benites},
url = {http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?pid=S1516-14392004000200020&script=sci_arttext},
year = {2004},
date = {2004-01-01},
journal = {Materials Research},
volume = {7},
number = {2},
pages = {339--342},
publisher = {SciELO Brasil},
abstract = {Metallic nanowires have attracted much attention in the last years due to new phenomena such as quantum conductance and the existence of unexpected long interatomic distances attaining 0.3-0.5 nm. These large distances represented a challenge for physical interpretation. In this work we present experimental data from high-resolution transmission electron microscopy and results from ab initio calculations for suspended gold chains and show that these large distances can be easily explained by the presence of carbon atoms as contaminants. In principle the present conclusions can be also applied to other metallic nanowires (such as Ag and Pt) whose structures also present large interatomic distances.},
keywords = {Contaminantes, Electronic Structure, Linear Atomic Chains, Metallic Nanowires, Structure},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Metallic nanowires have attracted much attention in the last years due to new phenomena such as quantum conductance and the existence of unexpected long interatomic distances attaining 0.3-0.5 nm. These large distances represented a challenge for physical interpretation. In this work we present experimental data from high-resolution transmission electron microscopy and results from ab initio calculations for suspended gold chains and show that these large distances can be easily explained by the presence of carbon atoms as contaminants. In principle the present conclusions can be also applied to other metallic nanowires (such as Ag and Pt) whose structures also present large interatomic distances.


