http://scholar.google.com/citations?hl=en&user=95SvbM8AAAAJ
Cristiano F Woellner Peter Samora Owuor, Tong Li
High Toughness in Ultralow Density Graphene Oxide Foam Journal Article
Em: Advanced Materials Interfaces, vol. 4, não 10, pp. 1700030, 2017.
@article{Owuor2017,
title = {High Toughness in Ultralow Density Graphene Oxide Foam},
author = {Peter Samora Owuor, Cristiano F Woellner, Tong Li, Soumya Vinod, Sehmus Ozden, Suppanat Kosolwattana, Sanjit Bhowmick, Luong Xuan Duy, Rodrigo V Salvatierra, Bingqing Wei, Syed AS Asif, James M Tour, Robert Vajtai, Jun Lou, Douglas S Galvão, Chandra Sekhar Tiwary, Pulickel Ajayan},
url = {http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/admi.201700030/abstract },
doi = {10.1002/admi.201700030},
year = {2017},
date = {2017-03-01},
journal = {Advanced Materials Interfaces},
volume = {4},
number = {10},
pages = {1700030},
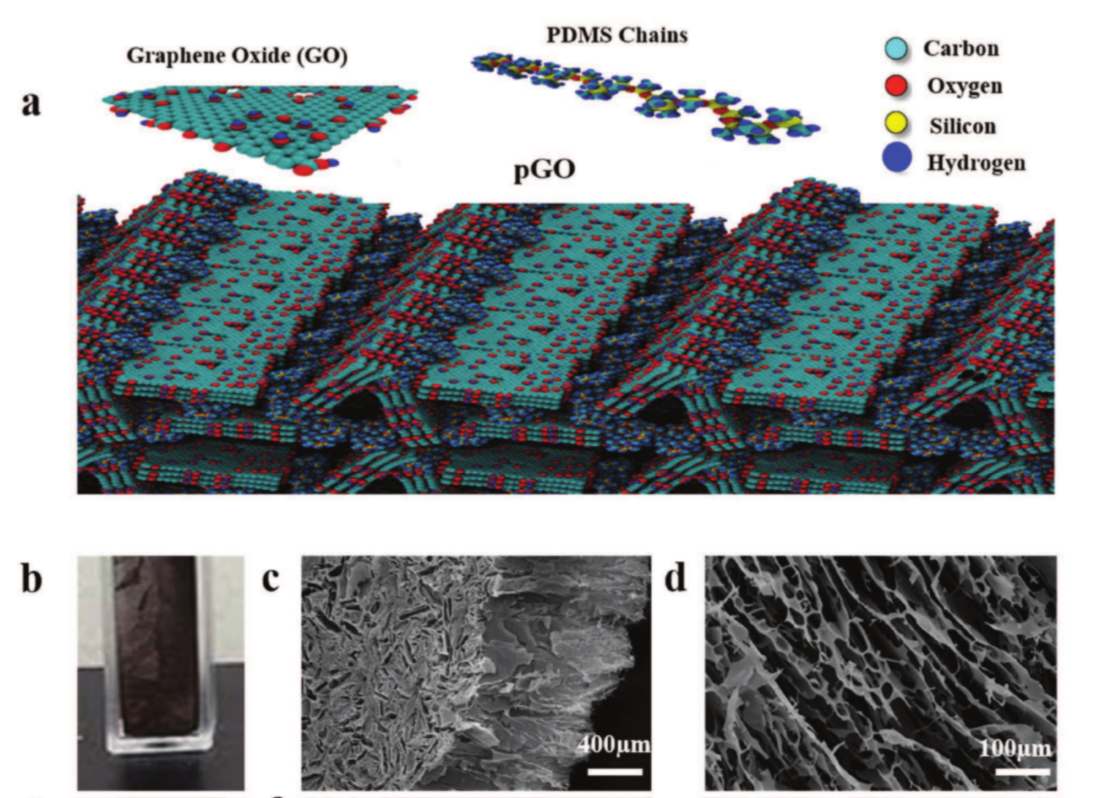
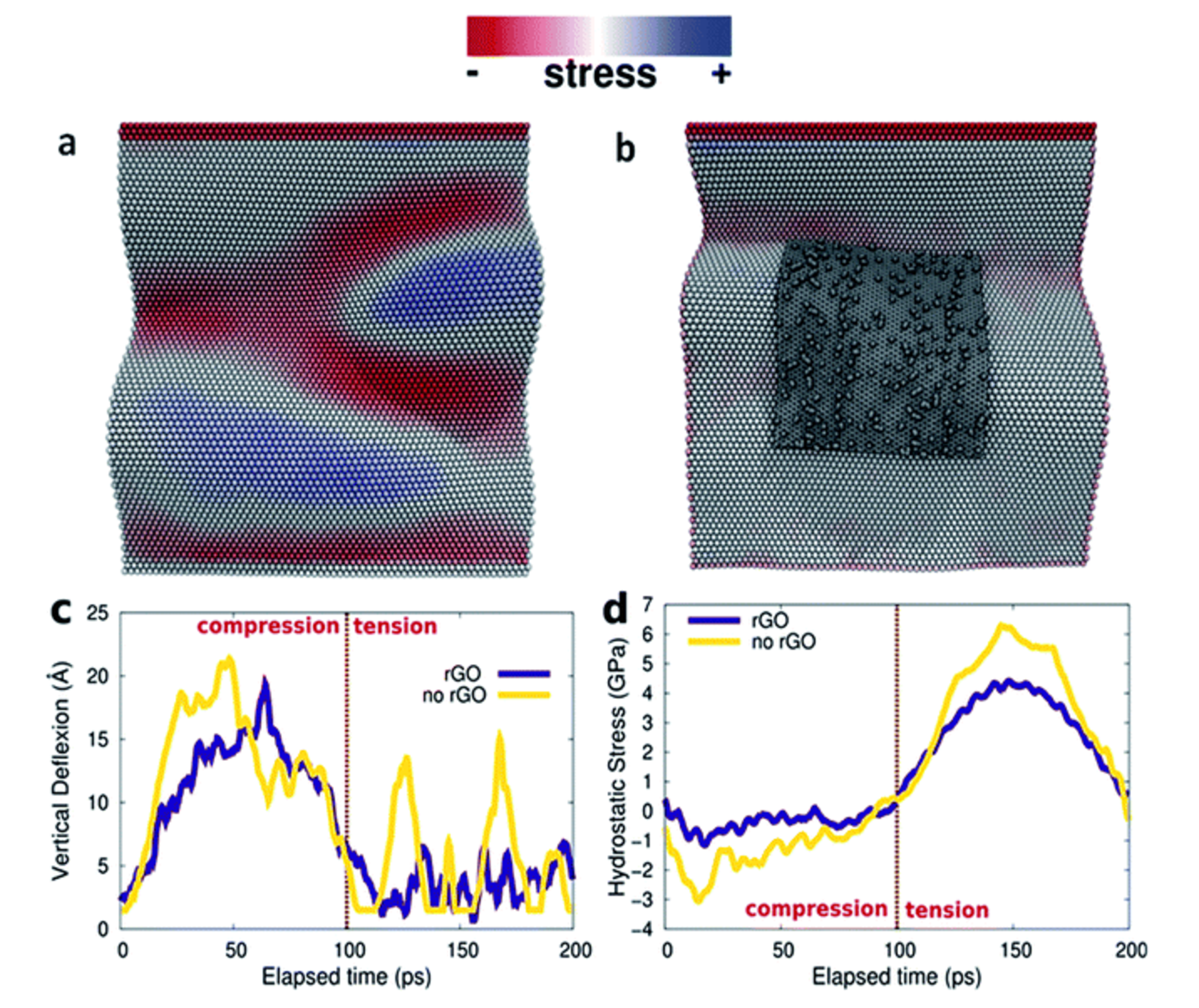
abstract = {Here, the scalable synthesis of low-density 3D macroscopic structure of graphene oxide (GO) interconnected with polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) is reported. A controlled amount of PDMS is infused into the freeze-dried foam to result into a very rigid structure with improved mechanical properties, such as tensile plasticity and toughness. The PDMS wets the graphene oxide sheets and acts like glue between the 2D sheets. Molecular dynamics simulations are used to further elucidate the mechanisms of the interactions of graphene oxide layers with PDMS. The ability of using the interconnecting graphene oxide foam as an effective oil–water separator and stable insulating behavior to elevated temperatures are further demonstrated. The structural rigidity of the sample is also tested using laser impact and compared with GO foam.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Chandra Sekhar Tiwary Sujin P Jose, Suppanat Kosolwattana
Enhanced supercapacitor performance of a 3D architecture tailored using atomically thin rGO–MoS 2 2D sheets Journal Article
Em: RSC Advances, vol. 6, pp. 93384-93393, 2016.
@article{Jose2016,
title = {Enhanced supercapacitor performance of a 3D architecture tailored using atomically thin rGO–MoS 2 2D sheets},
author = {Sujin P Jose, Chandra Sekhar Tiwary, Suppanat Kosolwattana, Prasanth Raghavan, Leonardo D Machado, Chandkiram Gautam, T Prasankumar, Jarin Joyner, Sehmus Ozden, Douglas S Galvao, PM Ajayan},
url = {xlink.rsc.org/?DOI=c6ra20960b},
doi = {10.1039/C6RA20960B},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-09-19},
journal = {RSC Advances},
volume = {6},
pages = {93384-93393},
abstract = {A 3D architecture is fabricated using 2D nano-sheets of GO and MoS2 as the building blocks by a facile, one-pot chronoamperometry method to achieve a conductive additive free, binder free and scalable supercapacitor electrode. The superior electrochemical properties of the 3D PPy-rGO–MoS2 (PGMo) are due to its porous structure, thin wall, high surface area and high electrical conductivity that endow rapid transportation of electrolyte ions and electrons throughout the electrode matrix. The synergistic effect between the components in a proper ratio improves the supercapacitor performance and material stability of PGMo. The possible correlation of the structure and electrochemical performance of the 3D ternary composite is backed by a fully atomistic molecular dynamics (MD) simulation study. The high specific capacitance (387 F g−1) and impressive cycling stability (>1000 cycles) estimated for PGMo open up an opportunity to consider the 3D ternary nanostructures as cutting edge materials for energy storage solutions.
},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Vinod, Soumya; Tiwary, Chandra Sekhar; Machado, Leonardo Dantas; Ozden, Sehmus; Shaw, Preston; Cho, Juny; Vajtai, Robert; Galvao, Douglas Soares; Ajayan, Pulickel M
Strain Rate Dependent Shear Plasticity in Graphite Oxide Journal Article
Em: Nano Letters, vol. 16, não 2, pp. 1127–1131, 2016.
@article{Vinod2016,
title = {Strain Rate Dependent Shear Plasticity in Graphite Oxide},
author = {Vinod, Soumya and Tiwary, Chandra Sekhar and Machado, Leonardo Dantas and Ozden, Sehmus and Shaw, Preston and Cho, Juny and Vajtai, Robert and Galvao, Douglas Soares and Ajayan, Pulickel M},
url = {http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b04346},
doi = {10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b04346},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-01-16},
journal = {Nano Letters},
volume = {16},
number = {2},
pages = {1127–1131},
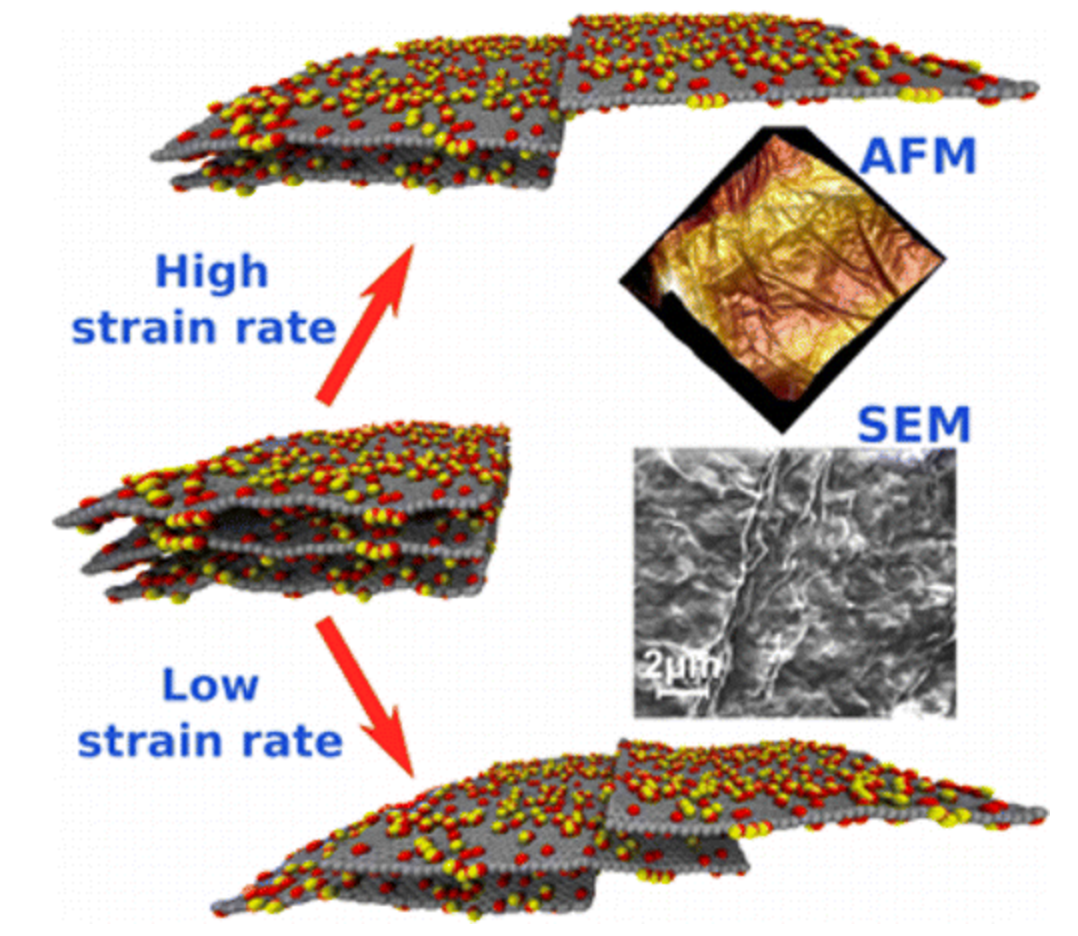
abstract = {Graphene oxide film is made of stacked graphene layers with chemical functionalities, and we report that plasticity in the film can be engineered by strain rate tuning. The deformation behavior and plasticity of such functionalized layered systems is dominated by shear slip between individual layers and interaction between functional groups. Stress–strain behavior and theoretical models suggest that the deformation is strongly strain rate dependent and undergoes brittle to ductile transition with decreasing strain rate.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2017
Cristiano F Woellner Peter Samora Owuor, Tong Li
High Toughness in Ultralow Density Graphene Oxide Foam Journal Article
Em: Advanced Materials Interfaces, vol. 4, não 10, pp. 1700030, 2017.
Resumo | Links | BibTeX | Tags: foams, graphene oxide, Mechanical Properties, Molecular Dynamics
@article{Owuor2017,
title = {High Toughness in Ultralow Density Graphene Oxide Foam},
author = {Peter Samora Owuor, Cristiano F Woellner, Tong Li, Soumya Vinod, Sehmus Ozden, Suppanat Kosolwattana, Sanjit Bhowmick, Luong Xuan Duy, Rodrigo V Salvatierra, Bingqing Wei, Syed AS Asif, James M Tour, Robert Vajtai, Jun Lou, Douglas S Galvão, Chandra Sekhar Tiwary, Pulickel Ajayan},
url = {http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/admi.201700030/abstract },
doi = {10.1002/admi.201700030},
year = {2017},
date = {2017-03-01},
journal = {Advanced Materials Interfaces},
volume = {4},
number = {10},
pages = {1700030},
abstract = {Here, the scalable synthesis of low-density 3D macroscopic structure of graphene oxide (GO) interconnected with polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) is reported. A controlled amount of PDMS is infused into the freeze-dried foam to result into a very rigid structure with improved mechanical properties, such as tensile plasticity and toughness. The PDMS wets the graphene oxide sheets and acts like glue between the 2D sheets. Molecular dynamics simulations are used to further elucidate the mechanisms of the interactions of graphene oxide layers with PDMS. The ability of using the interconnecting graphene oxide foam as an effective oil–water separator and stable insulating behavior to elevated temperatures are further demonstrated. The structural rigidity of the sample is also tested using laser impact and compared with GO foam.},
keywords = {foams, graphene oxide, Mechanical Properties, Molecular Dynamics},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2016
Chandra Sekhar Tiwary Sujin P Jose, Suppanat Kosolwattana
Enhanced supercapacitor performance of a 3D architecture tailored using atomically thin rGO–MoS 2 2D sheets Journal Article
Em: RSC Advances, vol. 6, pp. 93384-93393, 2016.
Resumo | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Chalcogenides, DFT, graphene oxide, Molecular Dynamics
@article{Jose2016,
title = {Enhanced supercapacitor performance of a 3D architecture tailored using atomically thin rGO–MoS 2 2D sheets},
author = {Sujin P Jose, Chandra Sekhar Tiwary, Suppanat Kosolwattana, Prasanth Raghavan, Leonardo D Machado, Chandkiram Gautam, T Prasankumar, Jarin Joyner, Sehmus Ozden, Douglas S Galvao, PM Ajayan},
url = {xlink.rsc.org/?DOI=c6ra20960b},
doi = {10.1039/C6RA20960B},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-09-19},
journal = {RSC Advances},
volume = {6},
pages = {93384-93393},
abstract = {A 3D architecture is fabricated using 2D nano-sheets of GO and MoS2 as the building blocks by a facile, one-pot chronoamperometry method to achieve a conductive additive free, binder free and scalable supercapacitor electrode. The superior electrochemical properties of the 3D PPy-rGO–MoS2 (PGMo) are due to its porous structure, thin wall, high surface area and high electrical conductivity that endow rapid transportation of electrolyte ions and electrons throughout the electrode matrix. The synergistic effect between the components in a proper ratio improves the supercapacitor performance and material stability of PGMo. The possible correlation of the structure and electrochemical performance of the 3D ternary composite is backed by a fully atomistic molecular dynamics (MD) simulation study. The high specific capacitance (387 F g−1) and impressive cycling stability (>1000 cycles) estimated for PGMo open up an opportunity to consider the 3D ternary nanostructures as cutting edge materials for energy storage solutions.
},
keywords = {Chalcogenides, DFT, graphene oxide, Molecular Dynamics},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Vinod, Soumya; Tiwary, Chandra Sekhar; Machado, Leonardo Dantas; Ozden, Sehmus; Shaw, Preston; Cho, Juny; Vajtai, Robert; Galvao, Douglas Soares; Ajayan, Pulickel M
Strain Rate Dependent Shear Plasticity in Graphite Oxide Journal Article
Em: Nano Letters, vol. 16, não 2, pp. 1127–1131, 2016.
Resumo | Links | BibTeX | Tags: graphene oxide, Molecular Dynamics, plasticity
@article{Vinod2016,
title = {Strain Rate Dependent Shear Plasticity in Graphite Oxide},
author = {Vinod, Soumya and Tiwary, Chandra Sekhar and Machado, Leonardo Dantas and Ozden, Sehmus and Shaw, Preston and Cho, Juny and Vajtai, Robert and Galvao, Douglas Soares and Ajayan, Pulickel M},
url = {http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b04346},
doi = {10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b04346},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-01-16},
journal = {Nano Letters},
volume = {16},
number = {2},
pages = {1127–1131},
abstract = {Graphene oxide film is made of stacked graphene layers with chemical functionalities, and we report that plasticity in the film can be engineered by strain rate tuning. The deformation behavior and plasticity of such functionalized layered systems is dominated by shear slip between individual layers and interaction between functional groups. Stress–strain behavior and theoretical models suggest that the deformation is strongly strain rate dependent and undergoes brittle to ductile transition with decreasing strain rate.},
keywords = {graphene oxide, Molecular Dynamics, plasticity},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}


