http://scholar.google.com/citations?hl=en&user=95SvbM8AAAAJ
PAS Autreto MJ Lagos, J Bettini
Surface effects on the mechanical elongation of AuCu nanowires: De-alloying and the formation of mixed suspended atomic chains Journal Article
Em: Journal of Applied Physics, vol. 117, não 9, pp. 094301, 2015.
@article{Lagos2015,
title = {Surface effects on the mechanical elongation of AuCu nanowires: De-alloying and the formation of mixed suspended atomic chains},
author = {MJ Lagos, PAS Autreto, J Bettini, F Sato, SO Dantas, DS Galvao, D Ugarte},
url = {http://scitation.aip.org/content/aip/journal/jap/117/9/10.1063/1.4913625},
doi = {10.1063/1.4913625},
year = {2015},
date = {2015-03-07},
journal = {Journal of Applied Physics},
volume = {117},
number = {9},
pages = {094301},
abstract = {We report here an atomistic study of the mechanical deformation of Au x Cu (1− x ) atomic-size wires (nanowires (NWs)) by means of high resolution transmission electron microscopy experiments. Molecular dynamics simulations were also carried out in order to obtain deeper insights on the dynamical properties of stretched NWs. The mechanical properties are significantly dependent on the chemical composition that evolves in time at the junction; some structures exhibit a remarkable de-alloying behavior. Also, our results represent the first experimental realization of mixed linear atomic chains (LACs) among transition and noble metals; in particular, surface energies induce chemical gradients on NW surfaces that can be exploited to control the relative LAC compositions (different number of gold and copper atoms). The implications of these results for nanocatalysis and spin transport of one-atom-thick metal wires are addressed.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Sato, Fernando; Braga, Scheila F; Santos, Helio F dos; Galvao, Douglas S
Structure-Activity Relationship Investigation of Some New Tetracyclines by Electronic Index Methodology Journal Article
Em: arXiv preprint arXiv:0708.2931, 2007.
@article{sato2007structure,
title = {Structure-Activity Relationship Investigation of Some New Tetracyclines by Electronic Index Methodology},
author = {Sato, Fernando and Braga, Scheila F and Santos, Helio F dos and Galvao, Douglas S},
url = {http://arxiv.org/abs/0708.2931},
year = {2007},
date = {2007-01-01},
journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:0708.2931},
abstract = {Tetracyclines are an old class of molecules that constitute a broad-spectrum antibiotics. Since the first member of tetracycline family were isolated, the clinical importance of these compounds as therapeutic and prophylactic agents against a wide range of infections has stimulated efforts to define their mode of action as inhibitors of bacterial reproduction. We used three SAR methodologies for the analysis of biological activity of a set of 104 tetracycline compounds. Our calculation were carried out using the semi-empirical Austin Method One (AM1) and Parametric Method 3 (PM3). Electronic Indices Methodology (EIM), Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) were applied to the classification of 14 old and 90 new proposed derivatives of tetracyclines. Our results make evident the importance of EIM descriptors in pattern recognition and also show that the EIM can be effectively used to predict the biological activity of Tetracyclines.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Troche, Karla S; Braga, Scheila F; Coluci, Vitor R; Galvao, Douglas S
Carcinogenic classification of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons through theoretical descriptors Journal Article
Em: International journal of quantum chemistry, vol. 103, não 5, pp. 718–730, 2005.
@article{troche2005carcinogenic,
title = {Carcinogenic classification of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons through theoretical descriptors},
author = {Troche, Karla S and Braga, Scheila F and Coluci, Vitor R and Galvao, Douglas S},
url = {http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/qua.20529/full},
year = {2005},
date = {2005-01-01},
journal = {International journal of quantum chemistry},
volume = {103},
number = {5},
pages = {718--730},
publisher = {Wiley Online Library},
abstract = {Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) constitute an importantfamily of molecules capable of inducing chemical carcinogenesis. In this work we reporta comparative structure–activity relationship (SAR) study for 81 PAHs using differentmethodologies. The recently developed electronic indices methodology (EIM) withquantum descriptors obtained from different semiempirical methods (AM1, PM3, andPM5) was contrasted against more standard pattern recognition methods (PRMs),principal component analysis (PCA), hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA), Kth nearestneighbor (KNN), soft independent modeling of class analogies (SIMCA), and neuralnetworks (NN). Our results show that PRMs validate the statistical value of electronicparameters derived from EIM analysis and their ability to identify active compounds.EIM outperformed more standard SAR methodologies and does not appear to besignificantly Hamiltonian-dependent.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Braga, Scheila Furtado; Galvao, Douglas Soares
Benzo [c] quinolizin-3-ones theoretical investigation: SAR analysis and application to nontested compounds Journal Article
Em: Journal of chemical information and computer sciences, vol. 44, não 6, pp. 1987–1997, 2004.
@article{braga2004benzo,
title = {Benzo [c] quinolizin-3-ones theoretical investigation: SAR analysis and application to nontested compounds},
author = {Braga, Scheila Furtado and Galvao, Douglas Soares},
url = {http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ci049837u},
year = {2004},
date = {2004-01-01},
journal = {Journal of chemical information and computer sciences},
volume = {44},
number = {6},
pages = {1987--1997},
publisher = {American Chemical Society},
abstract = {We investigate with the use of theoretical methodologies the activity of a set of 41 benzo[c]quinolizin-3-
ones (BC3), some of them explored as selective inhibitors of the human 5R-reductase steroid. For the
structure-activity study we have considered dividing the molecules into groups of tested and nontested
compounds. Semiempirical calculations and pattern recognition methods such as Electronic Indices
Methodology (EIM), Principal Components Analysis (PCA), Hierarchical Cluster Analysis (HCA), and
K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) have been applied to search for a correlation between experimental activity
and theoretical descriptors. Our results show that it is possible to directly correlate some molecular quantum
descriptors with BC3 biological activity. This information can be used in principle to identify active/inactive
untested compounds and/or to design new active compounds.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
ones (BC3), some of them explored as selective inhibitors of the human 5R-reductase steroid. For the
structure-activity study we have considered dividing the molecules into groups of tested and nontested
compounds. Semiempirical calculations and pattern recognition methods such as Electronic Indices
Methodology (EIM), Principal Components Analysis (PCA), Hierarchical Cluster Analysis (HCA), and
K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) have been applied to search for a correlation between experimental activity
and theoretical descriptors. Our results show that it is possible to directly correlate some molecular quantum
descriptors with BC3 biological activity. This information can be used in principle to identify active/inactive
untested compounds and/or to design new active compounds.
Braga, Scheila Furtado; Galvao, Douglas Soares
A structure-activity study of taxol, taxotere, and derivatives using the electronic indices methodology (EIM) Journal Article
Em: Journal of chemical information and computer sciences, vol. 43, não 2, pp. 699–706, 2003.
@article{braga2003structure,
title = {A structure-activity study of taxol, taxotere, and derivatives using the electronic indices methodology (EIM)},
author = {Braga, Scheila Furtado and Galvao, Douglas Soares},
url = {http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ci025640v},
year = {2003},
date = {2003-01-01},
journal = {Journal of chemical information and computer sciences},
volume = {43},
number = {2},
pages = {699--706},
publisher = {American Chemical Society},
abstract = {Among the new families of effective anticancer drugs, the natural product paclitaxel (Taxol/Bristol-MyersSquibb)
and its semisynthetic derivative docetaxel (Taxotere/Rhone-Poulenc Rorer) are probably the most
promising agents under investigation. Surprisingly considering their importance no detailed quantum
mechanical studies have been carried out for these drugs. In this work we report the first structure-activity
relationship (SAR) studies for 20 taxoid structures using molecular descriptors from all-electron quantum
methods. The used methods were the pattern-recognition Principal Component Analysis (PCA), Hierarchical
Clustering Analysis (HCA), and the recently developed Electronic Indices Methodology (EIM). The combined
use of EIM with PCA/HCA methodologies was able to correctly classify active and inactive taxoids with
100% of accuracy using only a few “universal” quantum molecular descriptors. It was possible to identify
the electronic features defining active molecules. This information can be used to select and design new
active compounds. The combined use of EIM with PCA/HCA can be a new and very efficient tool in the
field of computer assisted drug design.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
and its semisynthetic derivative docetaxel (Taxotere/Rhone-Poulenc Rorer) are probably the most
promising agents under investigation. Surprisingly considering their importance no detailed quantum
mechanical studies have been carried out for these drugs. In this work we report the first structure-activity
relationship (SAR) studies for 20 taxoid structures using molecular descriptors from all-electron quantum
methods. The used methods were the pattern-recognition Principal Component Analysis (PCA), Hierarchical
Clustering Analysis (HCA), and the recently developed Electronic Indices Methodology (EIM). The combined
use of EIM with PCA/HCA methodologies was able to correctly classify active and inactive taxoids with
100% of accuracy using only a few “universal” quantum molecular descriptors. It was possible to identify
the electronic features defining active molecules. This information can be used to select and design new
active compounds. The combined use of EIM with PCA/HCA can be a new and very efficient tool in the
field of computer assisted drug design.
Braga, SF; Galvao, DS
A semiempirical study on the electronic structure of 10-deacetylbaccatin-III Journal Article
Em: Journal of Molecular Graphics and Modelling, vol. 21, não 1, pp. 57–70, 2002.
@article{braga2002semiempirical,
title = {A semiempirical study on the electronic structure of 10-deacetylbaccatin-III},
author = {Braga, SF and Galvao, DS},
url = {http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1093326302001213},
year = {2002},
date = {2002-01-01},
journal = {Journal of Molecular Graphics and Modelling},
volume = {21},
number = {1},
pages = {57--70},
publisher = {Elsevier},
abstract = {We performed a conformational and electronic analysis for 10-deacetylbaccatin-III (DBAC) using well-known semiempirical methods (parametric method 3 (PM3) and Zerner’s intermediate neglect of differential overlap (ZINDO)) coupled to the concepts of total and local density of states (LDOS). Our results indicate that regions presented by paclitaxel (Taxol®) as important for the biological activity can be traced out by the electronic features present in DBAC. These molecules differ only by a phenylisoserine side chain. Compared to paclitaxel, DBAC has a simpler structure in terms of molecular size and number of degrees of freedom (d.f.). This makes DBAC a good candidate for a preliminary investigation of the taxoid family. Our results question the importance of the oxetane group, which seems to be consistent with recent experimental data.
},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Coluci, Vitor Rafael; Vendrame, Rosana; Braga, RS; Galvao, DS
Em: Journal of chemical information and computer sciences, vol. 42, não 6, pp. 1479–1489, 2002.
@article{coluci2002identifying,
title = {Identifying relevant molecular descriptors related to carcinogenic activity of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) using pattern recognition methods},
author = {Coluci, Vitor Rafael and Vendrame, Rosana and Braga, RS and Galvao, DS},
url = {http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ci025577%2B},
year = {2002},
date = {2002-01-01},
journal = {Journal of chemical information and computer sciences},
volume = {42},
number = {6},
pages = {1479--1489},
publisher = {American Chemical Society},
abstract = {Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) constitute an important family of molecules capable of inducing
chemical carcinogenesis. In this work we report structure-activity relationship (SAR) studies for 81 PAHs
using the pattern-recognition methods Principal Component Analysis (PCA), Hierarchical Clustering Analysis
(HCA) and Neural Networks (NN). The used molecular descriptors were obtained from the semiempirical
Parametric Method 3 (PM3) calculations. We have developed a new procedure that is capable of identifying
the PAHs’ carcinogenic activity with an accuracy higher than 80%. PCA selected molecular descriptors
that can be directly correlated with some models proposed to PAHs’ metabolic activation mechanism leading
to the formation of PAHs-DNA adducts. PCA, HCA and NN validate the energy separation between the
highest occupied molecular orbital and its next lower level as a major descriptor defining the carcinogenic
activity. This descriptor has been only recently discussed in the literature as one new possible universal
parameter for defining the biological activity of several classes of compounds.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
chemical carcinogenesis. In this work we report structure-activity relationship (SAR) studies for 81 PAHs
using the pattern-recognition methods Principal Component Analysis (PCA), Hierarchical Clustering Analysis
(HCA) and Neural Networks (NN). The used molecular descriptors were obtained from the semiempirical
Parametric Method 3 (PM3) calculations. We have developed a new procedure that is capable of identifying
the PAHs’ carcinogenic activity with an accuracy higher than 80%. PCA selected molecular descriptors
that can be directly correlated with some models proposed to PAHs’ metabolic activation mechanism leading
to the formation of PAHs-DNA adducts. PCA, HCA and NN validate the energy separation between the
highest occupied molecular orbital and its next lower level as a major descriptor defining the carcinogenic
activity. This descriptor has been only recently discussed in the literature as one new possible universal
parameter for defining the biological activity of several classes of compounds.
2015
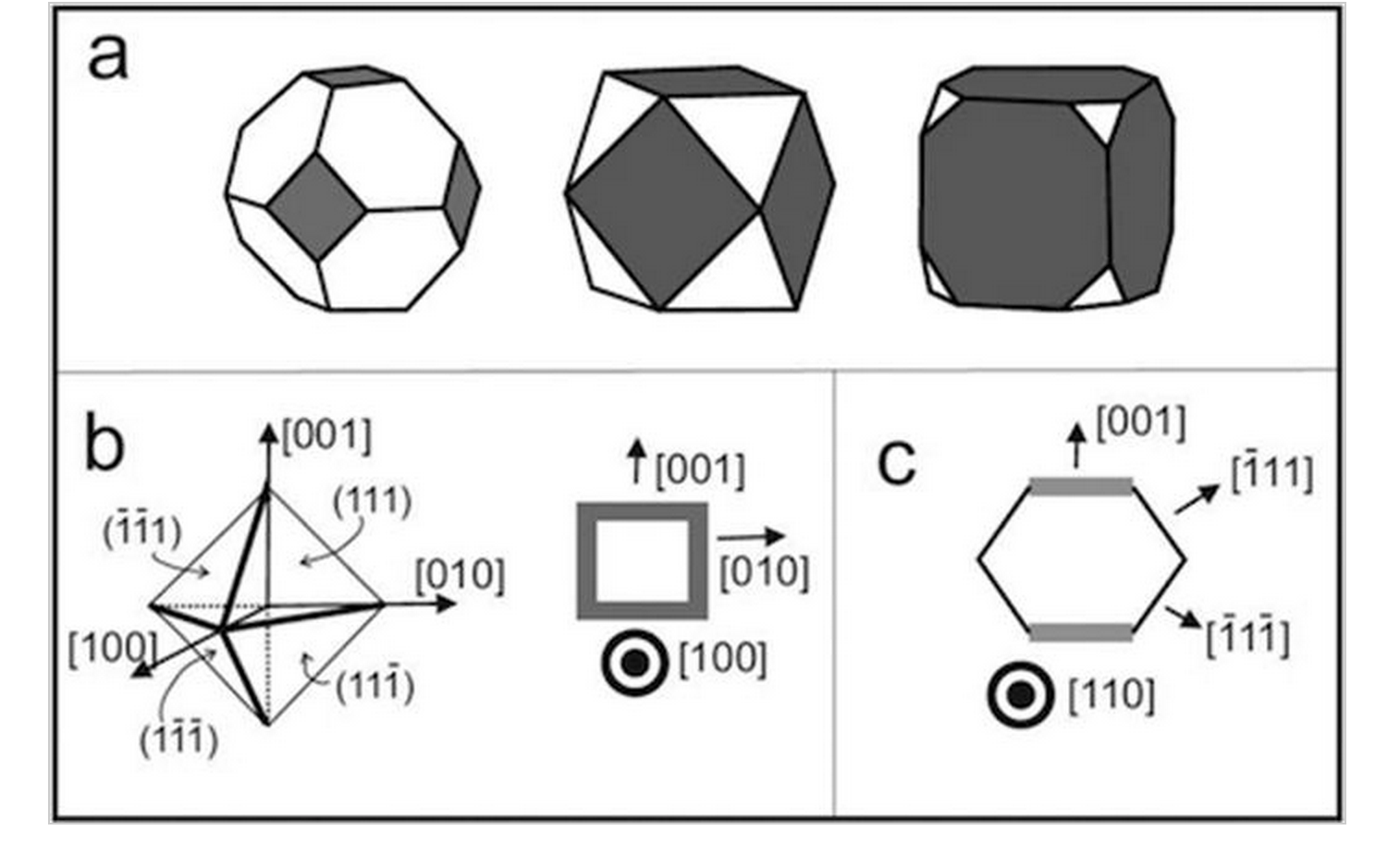
PAS Autreto MJ Lagos, J Bettini
Surface effects on the mechanical elongation of AuCu nanowires: De-alloying and the formation of mixed suspended atomic chains Journal Article
Em: Journal of Applied Physics, vol. 117, não 9, pp. 094301, 2015.
Resumo | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Metallic Nanowires, Molecular Dynamics, TEM, Theory of Electronic Indices
@article{Lagos2015,
title = {Surface effects on the mechanical elongation of AuCu nanowires: De-alloying and the formation of mixed suspended atomic chains},
author = {MJ Lagos, PAS Autreto, J Bettini, F Sato, SO Dantas, DS Galvao, D Ugarte},
url = {http://scitation.aip.org/content/aip/journal/jap/117/9/10.1063/1.4913625},
doi = {10.1063/1.4913625},
year = {2015},
date = {2015-03-07},
journal = {Journal of Applied Physics},
volume = {117},
number = {9},
pages = {094301},
abstract = {We report here an atomistic study of the mechanical deformation of Au x Cu (1− x ) atomic-size wires (nanowires (NWs)) by means of high resolution transmission electron microscopy experiments. Molecular dynamics simulations were also carried out in order to obtain deeper insights on the dynamical properties of stretched NWs. The mechanical properties are significantly dependent on the chemical composition that evolves in time at the junction; some structures exhibit a remarkable de-alloying behavior. Also, our results represent the first experimental realization of mixed linear atomic chains (LACs) among transition and noble metals; in particular, surface energies induce chemical gradients on NW surfaces that can be exploited to control the relative LAC compositions (different number of gold and copper atoms). The implications of these results for nanocatalysis and spin transport of one-atom-thick metal wires are addressed.},
keywords = {Metallic Nanowires, Molecular Dynamics, TEM, Theory of Electronic Indices},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2007
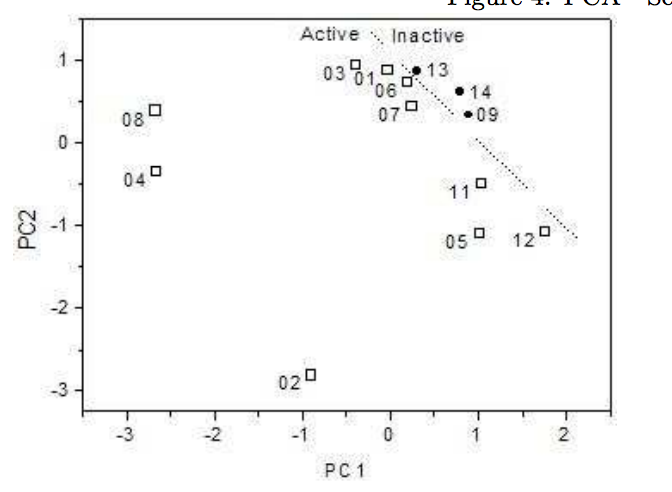
Sato, Fernando; Braga, Scheila F; Santos, Helio F dos; Galvao, Douglas S
Structure-Activity Relationship Investigation of Some New Tetracyclines by Electronic Index Methodology Journal Article
Em: arXiv preprint arXiv:0708.2931, 2007.
Resumo | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Drug Design, Electronic Structure, Neural Networks, PCA/HCA, Tetracyclines, Theory of Electronic Indices
@article{sato2007structure,
title = {Structure-Activity Relationship Investigation of Some New Tetracyclines by Electronic Index Methodology},
author = {Sato, Fernando and Braga, Scheila F and Santos, Helio F dos and Galvao, Douglas S},
url = {http://arxiv.org/abs/0708.2931},
year = {2007},
date = {2007-01-01},
journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:0708.2931},
abstract = {Tetracyclines are an old class of molecules that constitute a broad-spectrum antibiotics. Since the first member of tetracycline family were isolated, the clinical importance of these compounds as therapeutic and prophylactic agents against a wide range of infections has stimulated efforts to define their mode of action as inhibitors of bacterial reproduction. We used three SAR methodologies for the analysis of biological activity of a set of 104 tetracycline compounds. Our calculation were carried out using the semi-empirical Austin Method One (AM1) and Parametric Method 3 (PM3). Electronic Indices Methodology (EIM), Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) were applied to the classification of 14 old and 90 new proposed derivatives of tetracyclines. Our results make evident the importance of EIM descriptors in pattern recognition and also show that the EIM can be effectively used to predict the biological activity of Tetracyclines.},
keywords = {Drug Design, Electronic Structure, Neural Networks, PCA/HCA, Tetracyclines, Theory of Electronic Indices},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2005
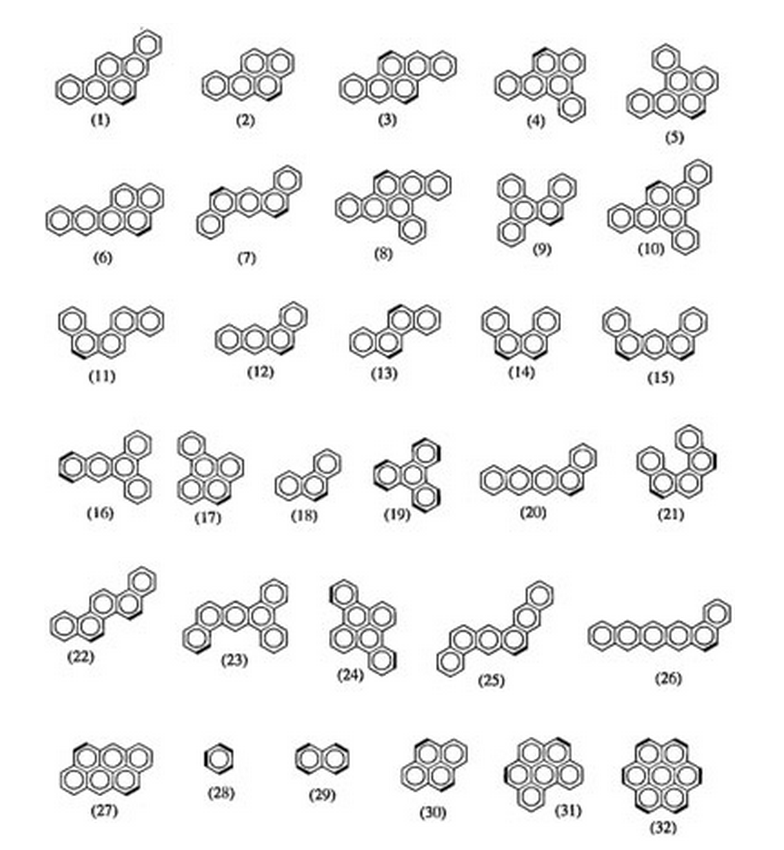
Troche, Karla S; Braga, Scheila F; Coluci, Vitor R; Galvao, Douglas S
Carcinogenic classification of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons through theoretical descriptors Journal Article
Em: International journal of quantum chemistry, vol. 103, não 5, pp. 718–730, 2005.
Resumo | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Carcinogenesis, HCA, Neural Networks, PCA, Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs), Theory of Electronic Indices
@article{troche2005carcinogenic,
title = {Carcinogenic classification of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons through theoretical descriptors},
author = {Troche, Karla S and Braga, Scheila F and Coluci, Vitor R and Galvao, Douglas S},
url = {http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/qua.20529/full},
year = {2005},
date = {2005-01-01},
journal = {International journal of quantum chemistry},
volume = {103},
number = {5},
pages = {718--730},
publisher = {Wiley Online Library},
abstract = {Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) constitute an importantfamily of molecules capable of inducing chemical carcinogenesis. In this work we reporta comparative structure–activity relationship (SAR) study for 81 PAHs using differentmethodologies. The recently developed electronic indices methodology (EIM) withquantum descriptors obtained from different semiempirical methods (AM1, PM3, andPM5) was contrasted against more standard pattern recognition methods (PRMs),principal component analysis (PCA), hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA), Kth nearestneighbor (KNN), soft independent modeling of class analogies (SIMCA), and neuralnetworks (NN). Our results show that PRMs validate the statistical value of electronicparameters derived from EIM analysis and their ability to identify active compounds.EIM outperformed more standard SAR methodologies and does not appear to besignificantly Hamiltonian-dependent.},
keywords = {Carcinogenesis, HCA, Neural Networks, PCA, Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs), Theory of Electronic Indices},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2004
![Benzo [c] quinolizin-3-ones theoretical investigation: SAR analysis and application to nontested compounds](https://sites.ifi.unicamp.br/galvao/files/2015/02/Screen-Shot-2015-02-26-at-12.21.40-PM.png)
Braga, Scheila Furtado; Galvao, Douglas Soares
Benzo [c] quinolizin-3-ones theoretical investigation: SAR analysis and application to nontested compounds Journal Article
Em: Journal of chemical information and computer sciences, vol. 44, não 6, pp. 1987–1997, 2004.
Resumo | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Drug Design, Electronic Structure, PCA/HCA, Theory of Electronic Indices
@article{braga2004benzo,
title = {Benzo [c] quinolizin-3-ones theoretical investigation: SAR analysis and application to nontested compounds},
author = {Braga, Scheila Furtado and Galvao, Douglas Soares},
url = {http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ci049837u},
year = {2004},
date = {2004-01-01},
journal = {Journal of chemical information and computer sciences},
volume = {44},
number = {6},
pages = {1987--1997},
publisher = {American Chemical Society},
abstract = {We investigate with the use of theoretical methodologies the activity of a set of 41 benzo[c]quinolizin-3-
ones (BC3), some of them explored as selective inhibitors of the human 5R-reductase steroid. For the
structure-activity study we have considered dividing the molecules into groups of tested and nontested
compounds. Semiempirical calculations and pattern recognition methods such as Electronic Indices
Methodology (EIM), Principal Components Analysis (PCA), Hierarchical Cluster Analysis (HCA), and
K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) have been applied to search for a correlation between experimental activity
and theoretical descriptors. Our results show that it is possible to directly correlate some molecular quantum
descriptors with BC3 biological activity. This information can be used in principle to identify active/inactive
untested compounds and/or to design new active compounds.},
keywords = {Drug Design, Electronic Structure, PCA/HCA, Theory of Electronic Indices},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
ones (BC3), some of them explored as selective inhibitors of the human 5R-reductase steroid. For the
structure-activity study we have considered dividing the molecules into groups of tested and nontested
compounds. Semiempirical calculations and pattern recognition methods such as Electronic Indices
Methodology (EIM), Principal Components Analysis (PCA), Hierarchical Cluster Analysis (HCA), and
K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) have been applied to search for a correlation between experimental activity
and theoretical descriptors. Our results show that it is possible to directly correlate some molecular quantum
descriptors with BC3 biological activity. This information can be used in principle to identify active/inactive
untested compounds and/or to design new active compounds.
2003
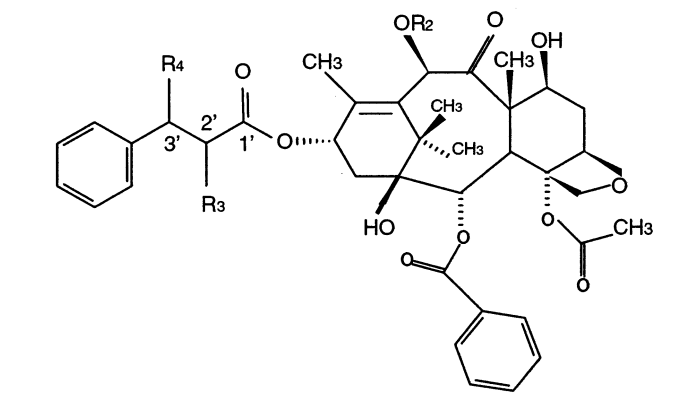
Braga, Scheila Furtado; Galvao, Douglas Soares
A structure-activity study of taxol, taxotere, and derivatives using the electronic indices methodology (EIM) Journal Article
Em: Journal of chemical information and computer sciences, vol. 43, não 2, pp. 699–706, 2003.
Resumo | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Drug Design, Electronic Structure, Taxol, Taxotere, Theory of Electronic Indices
@article{braga2003structure,
title = {A structure-activity study of taxol, taxotere, and derivatives using the electronic indices methodology (EIM)},
author = {Braga, Scheila Furtado and Galvao, Douglas Soares},
url = {http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ci025640v},
year = {2003},
date = {2003-01-01},
journal = {Journal of chemical information and computer sciences},
volume = {43},
number = {2},
pages = {699--706},
publisher = {American Chemical Society},
abstract = {Among the new families of effective anticancer drugs, the natural product paclitaxel (Taxol/Bristol-MyersSquibb)
and its semisynthetic derivative docetaxel (Taxotere/Rhone-Poulenc Rorer) are probably the most
promising agents under investigation. Surprisingly considering their importance no detailed quantum
mechanical studies have been carried out for these drugs. In this work we report the first structure-activity
relationship (SAR) studies for 20 taxoid structures using molecular descriptors from all-electron quantum
methods. The used methods were the pattern-recognition Principal Component Analysis (PCA), Hierarchical
Clustering Analysis (HCA), and the recently developed Electronic Indices Methodology (EIM). The combined
use of EIM with PCA/HCA methodologies was able to correctly classify active and inactive taxoids with
100% of accuracy using only a few “universal” quantum molecular descriptors. It was possible to identify
the electronic features defining active molecules. This information can be used to select and design new
active compounds. The combined use of EIM with PCA/HCA can be a new and very efficient tool in the
field of computer assisted drug design.},
keywords = {Drug Design, Electronic Structure, Taxol, Taxotere, Theory of Electronic Indices},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
and its semisynthetic derivative docetaxel (Taxotere/Rhone-Poulenc Rorer) are probably the most
promising agents under investigation. Surprisingly considering their importance no detailed quantum
mechanical studies have been carried out for these drugs. In this work we report the first structure-activity
relationship (SAR) studies for 20 taxoid structures using molecular descriptors from all-electron quantum
methods. The used methods were the pattern-recognition Principal Component Analysis (PCA), Hierarchical
Clustering Analysis (HCA), and the recently developed Electronic Indices Methodology (EIM). The combined
use of EIM with PCA/HCA methodologies was able to correctly classify active and inactive taxoids with
100% of accuracy using only a few “universal” quantum molecular descriptors. It was possible to identify
the electronic features defining active molecules. This information can be used to select and design new
active compounds. The combined use of EIM with PCA/HCA can be a new and very efficient tool in the
field of computer assisted drug design.
2002
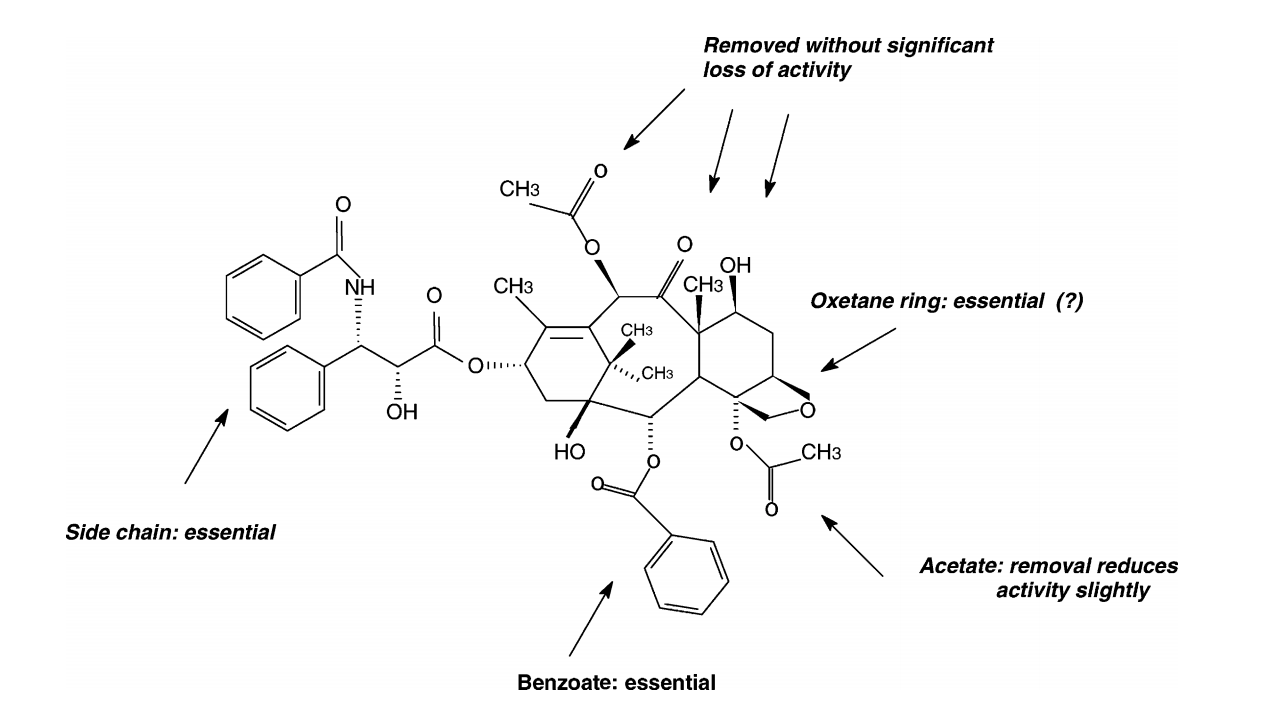
Braga, SF; Galvao, DS
A semiempirical study on the electronic structure of 10-deacetylbaccatin-III Journal Article
Em: Journal of Molecular Graphics and Modelling, vol. 21, não 1, pp. 57–70, 2002.
Resumo | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Baccatin, Drug Design, Electronic Structure, Taxol, Taxotere, Theory of Electronic Indices
@article{braga2002semiempirical,
title = {A semiempirical study on the electronic structure of 10-deacetylbaccatin-III},
author = {Braga, SF and Galvao, DS},
url = {http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1093326302001213},
year = {2002},
date = {2002-01-01},
journal = {Journal of Molecular Graphics and Modelling},
volume = {21},
number = {1},
pages = {57--70},
publisher = {Elsevier},
abstract = {We performed a conformational and electronic analysis for 10-deacetylbaccatin-III (DBAC) using well-known semiempirical methods (parametric method 3 (PM3) and Zerner’s intermediate neglect of differential overlap (ZINDO)) coupled to the concepts of total and local density of states (LDOS). Our results indicate that regions presented by paclitaxel (Taxol®) as important for the biological activity can be traced out by the electronic features present in DBAC. These molecules differ only by a phenylisoserine side chain. Compared to paclitaxel, DBAC has a simpler structure in terms of molecular size and number of degrees of freedom (d.f.). This makes DBAC a good candidate for a preliminary investigation of the taxoid family. Our results question the importance of the oxetane group, which seems to be consistent with recent experimental data.
},
keywords = {Baccatin, Drug Design, Electronic Structure, Taxol, Taxotere, Theory of Electronic Indices},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
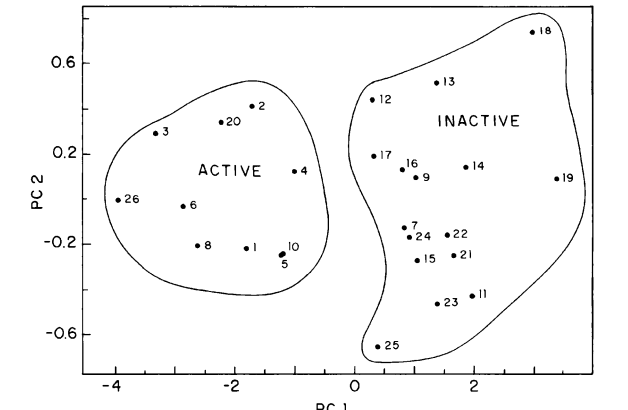
Coluci, Vitor Rafael; Vendrame, Rosana; Braga, RS; Galvao, DS
Em: Journal of chemical information and computer sciences, vol. 42, não 6, pp. 1479–1489, 2002.
Resumo | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Carcinogenesis, Neural Networks, PCA/HCA, Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs), Theory of Electronic Indices
@article{coluci2002identifying,
title = {Identifying relevant molecular descriptors related to carcinogenic activity of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) using pattern recognition methods},
author = {Coluci, Vitor Rafael and Vendrame, Rosana and Braga, RS and Galvao, DS},
url = {http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ci025577%2B},
year = {2002},
date = {2002-01-01},
journal = {Journal of chemical information and computer sciences},
volume = {42},
number = {6},
pages = {1479--1489},
publisher = {American Chemical Society},
abstract = {Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) constitute an important family of molecules capable of inducing
chemical carcinogenesis. In this work we report structure-activity relationship (SAR) studies for 81 PAHs
using the pattern-recognition methods Principal Component Analysis (PCA), Hierarchical Clustering Analysis
(HCA) and Neural Networks (NN). The used molecular descriptors were obtained from the semiempirical
Parametric Method 3 (PM3) calculations. We have developed a new procedure that is capable of identifying
the PAHs’ carcinogenic activity with an accuracy higher than 80%. PCA selected molecular descriptors
that can be directly correlated with some models proposed to PAHs’ metabolic activation mechanism leading
to the formation of PAHs-DNA adducts. PCA, HCA and NN validate the energy separation between the
highest occupied molecular orbital and its next lower level as a major descriptor defining the carcinogenic
activity. This descriptor has been only recently discussed in the literature as one new possible universal
parameter for defining the biological activity of several classes of compounds.},
keywords = {Carcinogenesis, Neural Networks, PCA/HCA, Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs), Theory of Electronic Indices},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
chemical carcinogenesis. In this work we report structure-activity relationship (SAR) studies for 81 PAHs
using the pattern-recognition methods Principal Component Analysis (PCA), Hierarchical Clustering Analysis
(HCA) and Neural Networks (NN). The used molecular descriptors were obtained from the semiempirical
Parametric Method 3 (PM3) calculations. We have developed a new procedure that is capable of identifying
the PAHs’ carcinogenic activity with an accuracy higher than 80%. PCA selected molecular descriptors
that can be directly correlated with some models proposed to PAHs’ metabolic activation mechanism leading
to the formation of PAHs-DNA adducts. PCA, HCA and NN validate the energy separation between the
highest occupied molecular orbital and its next lower level as a major descriptor defining the carcinogenic
activity. This descriptor has been only recently discussed in the literature as one new possible universal
parameter for defining the biological activity of several classes of compounds.


