http://scholar.google.com/citations?hl=en&user=95SvbM8AAAAJ
Sato, Fernando; Braga, Scheila F; Santos, Helio F dos; Galvao, Douglas S
Structure-Activity Relationship Investigation of Some New Tetracyclines by Electronic Index Methodology Journal Article
Em: arXiv preprint arXiv:0708.2931, 2007.
@article{sato2007structure,
title = {Structure-Activity Relationship Investigation of Some New Tetracyclines by Electronic Index Methodology},
author = {Sato, Fernando and Braga, Scheila F and Santos, Helio F dos and Galvao, Douglas S},
url = {http://arxiv.org/abs/0708.2931},
year = {2007},
date = {2007-01-01},
journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:0708.2931},
abstract = {Tetracyclines are an old class of molecules that constitute a broad-spectrum antibiotics. Since the first member of tetracycline family were isolated, the clinical importance of these compounds as therapeutic and prophylactic agents against a wide range of infections has stimulated efforts to define their mode of action as inhibitors of bacterial reproduction. We used three SAR methodologies for the analysis of biological activity of a set of 104 tetracycline compounds. Our calculation were carried out using the semi-empirical Austin Method One (AM1) and Parametric Method 3 (PM3). Electronic Indices Methodology (EIM), Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) were applied to the classification of 14 old and 90 new proposed derivatives of tetracyclines. Our results make evident the importance of EIM descriptors in pattern recognition and also show that the EIM can be effectively used to predict the biological activity of Tetracyclines.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Braga, Scheila Furtado; Galvao, Douglas Soares
Benzo [c] quinolizin-3-ones theoretical investigation: SAR analysis and application to nontested compounds Journal Article
Em: Journal of chemical information and computer sciences, vol. 44, não 6, pp. 1987–1997, 2004.
@article{braga2004benzo,
title = {Benzo [c] quinolizin-3-ones theoretical investigation: SAR analysis and application to nontested compounds},
author = {Braga, Scheila Furtado and Galvao, Douglas Soares},
url = {http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ci049837u},
year = {2004},
date = {2004-01-01},
journal = {Journal of chemical information and computer sciences},
volume = {44},
number = {6},
pages = {1987--1997},
publisher = {American Chemical Society},
abstract = {We investigate with the use of theoretical methodologies the activity of a set of 41 benzo[c]quinolizin-3-
ones (BC3), some of them explored as selective inhibitors of the human 5R-reductase steroid. For the
structure-activity study we have considered dividing the molecules into groups of tested and nontested
compounds. Semiempirical calculations and pattern recognition methods such as Electronic Indices
Methodology (EIM), Principal Components Analysis (PCA), Hierarchical Cluster Analysis (HCA), and
K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) have been applied to search for a correlation between experimental activity
and theoretical descriptors. Our results show that it is possible to directly correlate some molecular quantum
descriptors with BC3 biological activity. This information can be used in principle to identify active/inactive
untested compounds and/or to design new active compounds.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
ones (BC3), some of them explored as selective inhibitors of the human 5R-reductase steroid. For the
structure-activity study we have considered dividing the molecules into groups of tested and nontested
compounds. Semiempirical calculations and pattern recognition methods such as Electronic Indices
Methodology (EIM), Principal Components Analysis (PCA), Hierarchical Cluster Analysis (HCA), and
K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) have been applied to search for a correlation between experimental activity
and theoretical descriptors. Our results show that it is possible to directly correlate some molecular quantum
descriptors with BC3 biological activity. This information can be used in principle to identify active/inactive
untested compounds and/or to design new active compounds.
Braga, Scheila Furtado; Galvao, Douglas Soares
A structure-activity study of taxol, taxotere, and derivatives using the electronic indices methodology (EIM) Journal Article
Em: Journal of chemical information and computer sciences, vol. 43, não 2, pp. 699–706, 2003.
@article{braga2003structure,
title = {A structure-activity study of taxol, taxotere, and derivatives using the electronic indices methodology (EIM)},
author = {Braga, Scheila Furtado and Galvao, Douglas Soares},
url = {http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ci025640v},
year = {2003},
date = {2003-01-01},
journal = {Journal of chemical information and computer sciences},
volume = {43},
number = {2},
pages = {699--706},
publisher = {American Chemical Society},
abstract = {Among the new families of effective anticancer drugs, the natural product paclitaxel (Taxol/Bristol-MyersSquibb)
and its semisynthetic derivative docetaxel (Taxotere/Rhone-Poulenc Rorer) are probably the most
promising agents under investigation. Surprisingly considering their importance no detailed quantum
mechanical studies have been carried out for these drugs. In this work we report the first structure-activity
relationship (SAR) studies for 20 taxoid structures using molecular descriptors from all-electron quantum
methods. The used methods were the pattern-recognition Principal Component Analysis (PCA), Hierarchical
Clustering Analysis (HCA), and the recently developed Electronic Indices Methodology (EIM). The combined
use of EIM with PCA/HCA methodologies was able to correctly classify active and inactive taxoids with
100% of accuracy using only a few “universal” quantum molecular descriptors. It was possible to identify
the electronic features defining active molecules. This information can be used to select and design new
active compounds. The combined use of EIM with PCA/HCA can be a new and very efficient tool in the
field of computer assisted drug design.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
and its semisynthetic derivative docetaxel (Taxotere/Rhone-Poulenc Rorer) are probably the most
promising agents under investigation. Surprisingly considering their importance no detailed quantum
mechanical studies have been carried out for these drugs. In this work we report the first structure-activity
relationship (SAR) studies for 20 taxoid structures using molecular descriptors from all-electron quantum
methods. The used methods were the pattern-recognition Principal Component Analysis (PCA), Hierarchical
Clustering Analysis (HCA), and the recently developed Electronic Indices Methodology (EIM). The combined
use of EIM with PCA/HCA methodologies was able to correctly classify active and inactive taxoids with
100% of accuracy using only a few “universal” quantum molecular descriptors. It was possible to identify
the electronic features defining active molecules. This information can be used to select and design new
active compounds. The combined use of EIM with PCA/HCA can be a new and very efficient tool in the
field of computer assisted drug design.
Braga, SF; Galvao, DS
A semiempirical study on the electronic structure of 10-deacetylbaccatin-III Journal Article
Em: Journal of Molecular Graphics and Modelling, vol. 21, não 1, pp. 57–70, 2002.
@article{braga2002semiempirical,
title = {A semiempirical study on the electronic structure of 10-deacetylbaccatin-III},
author = {Braga, SF and Galvao, DS},
url = {http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1093326302001213},
year = {2002},
date = {2002-01-01},
journal = {Journal of Molecular Graphics and Modelling},
volume = {21},
number = {1},
pages = {57--70},
publisher = {Elsevier},
abstract = {We performed a conformational and electronic analysis for 10-deacetylbaccatin-III (DBAC) using well-known semiempirical methods (parametric method 3 (PM3) and Zerner’s intermediate neglect of differential overlap (ZINDO)) coupled to the concepts of total and local density of states (LDOS). Our results indicate that regions presented by paclitaxel (Taxol®) as important for the biological activity can be traced out by the electronic features present in DBAC. These molecules differ only by a phenylisoserine side chain. Compared to paclitaxel, DBAC has a simpler structure in terms of molecular size and number of degrees of freedom (d.f.). This makes DBAC a good candidate for a preliminary investigation of the taxoid family. Our results question the importance of the oxetane group, which seems to be consistent with recent experimental data.
},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Vendrame, R; Coluci, VR; Braga, RS; Galvao, DS
Structure--activity relationship (SAR) studies of the tripos benchmark steroids Journal Article
Em: Journal of Molecular Structure: THEOCHEM, vol. 619, não 1, pp. 195–205, 2002.
@article{vendrame2002structure,
title = {Structure--activity relationship (SAR) studies of the tripos benchmark steroids},
author = {Vendrame, R and Coluci, VR and Braga, RS and Galvao, DS},
url = {http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S016612800200578X},
year = {2002},
date = {2002-01-01},
journal = {Journal of Molecular Structure: THEOCHEM},
volume = {619},
number = {1},
pages = {195--205},
publisher = {Elsevier},
abstract = {We report here qualitative structure–activity relationship (SAR) studies for the molecular set called Tripos or Cramer steroid data set. These compounds are known to bind to corticosteroid binding globulin (CBG). In the present work we have used the electronic indices methodology (EIM). The EIM is based on Boolean relational rules exploring the concepts of local density of states and critical values for energy separation involving frontier orbitals. We have also carried out comparative principal component analysis (PCA) and hierarchical clustering analysis (HCA) studies with molecular descriptors obtained from EIM calculations. EIM, PCA and HCA correctly predict (100% accuracy) the steroid's biological activity. The present studies reinforce the universal applicability of the EIM descriptors and show that the combined use of EIM coupled to PCA can be a new efficient and powerful SAR tool.
},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2007
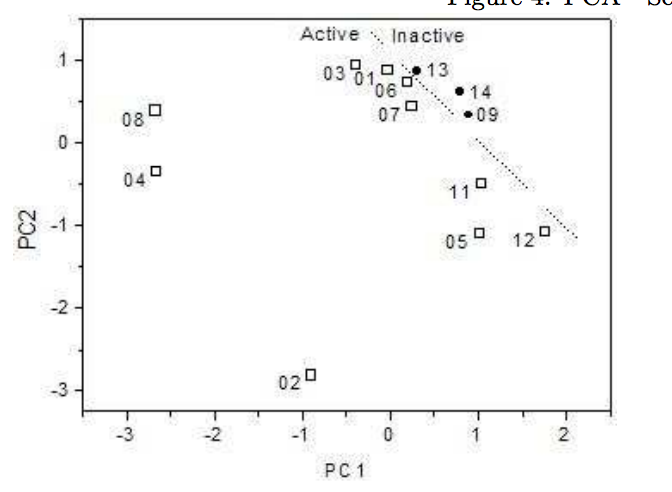
Sato, Fernando; Braga, Scheila F; Santos, Helio F dos; Galvao, Douglas S
Structure-Activity Relationship Investigation of Some New Tetracyclines by Electronic Index Methodology Journal Article
Em: arXiv preprint arXiv:0708.2931, 2007.
Resumo | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Drug Design, Electronic Structure, Neural Networks, PCA/HCA, Tetracyclines, Theory of Electronic Indices
@article{sato2007structure,
title = {Structure-Activity Relationship Investigation of Some New Tetracyclines by Electronic Index Methodology},
author = {Sato, Fernando and Braga, Scheila F and Santos, Helio F dos and Galvao, Douglas S},
url = {http://arxiv.org/abs/0708.2931},
year = {2007},
date = {2007-01-01},
journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:0708.2931},
abstract = {Tetracyclines are an old class of molecules that constitute a broad-spectrum antibiotics. Since the first member of tetracycline family were isolated, the clinical importance of these compounds as therapeutic and prophylactic agents against a wide range of infections has stimulated efforts to define their mode of action as inhibitors of bacterial reproduction. We used three SAR methodologies for the analysis of biological activity of a set of 104 tetracycline compounds. Our calculation were carried out using the semi-empirical Austin Method One (AM1) and Parametric Method 3 (PM3). Electronic Indices Methodology (EIM), Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) were applied to the classification of 14 old and 90 new proposed derivatives of tetracyclines. Our results make evident the importance of EIM descriptors in pattern recognition and also show that the EIM can be effectively used to predict the biological activity of Tetracyclines.},
keywords = {Drug Design, Electronic Structure, Neural Networks, PCA/HCA, Tetracyclines, Theory of Electronic Indices},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2004
![Benzo [c] quinolizin-3-ones theoretical investigation: SAR analysis and application to nontested compounds](https://sites.ifi.unicamp.br/galvao/files/2015/02/Screen-Shot-2015-02-26-at-12.21.40-PM.png)
Braga, Scheila Furtado; Galvao, Douglas Soares
Benzo [c] quinolizin-3-ones theoretical investigation: SAR analysis and application to nontested compounds Journal Article
Em: Journal of chemical information and computer sciences, vol. 44, não 6, pp. 1987–1997, 2004.
Resumo | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Drug Design, Electronic Structure, PCA/HCA, Theory of Electronic Indices
@article{braga2004benzo,
title = {Benzo [c] quinolizin-3-ones theoretical investigation: SAR analysis and application to nontested compounds},
author = {Braga, Scheila Furtado and Galvao, Douglas Soares},
url = {http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ci049837u},
year = {2004},
date = {2004-01-01},
journal = {Journal of chemical information and computer sciences},
volume = {44},
number = {6},
pages = {1987--1997},
publisher = {American Chemical Society},
abstract = {We investigate with the use of theoretical methodologies the activity of a set of 41 benzo[c]quinolizin-3-
ones (BC3), some of them explored as selective inhibitors of the human 5R-reductase steroid. For the
structure-activity study we have considered dividing the molecules into groups of tested and nontested
compounds. Semiempirical calculations and pattern recognition methods such as Electronic Indices
Methodology (EIM), Principal Components Analysis (PCA), Hierarchical Cluster Analysis (HCA), and
K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) have been applied to search for a correlation between experimental activity
and theoretical descriptors. Our results show that it is possible to directly correlate some molecular quantum
descriptors with BC3 biological activity. This information can be used in principle to identify active/inactive
untested compounds and/or to design new active compounds.},
keywords = {Drug Design, Electronic Structure, PCA/HCA, Theory of Electronic Indices},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
ones (BC3), some of them explored as selective inhibitors of the human 5R-reductase steroid. For the
structure-activity study we have considered dividing the molecules into groups of tested and nontested
compounds. Semiempirical calculations and pattern recognition methods such as Electronic Indices
Methodology (EIM), Principal Components Analysis (PCA), Hierarchical Cluster Analysis (HCA), and
K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) have been applied to search for a correlation between experimental activity
and theoretical descriptors. Our results show that it is possible to directly correlate some molecular quantum
descriptors with BC3 biological activity. This information can be used in principle to identify active/inactive
untested compounds and/or to design new active compounds.
2003
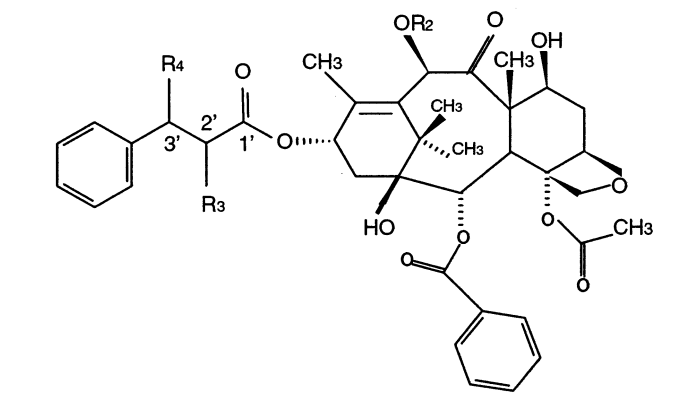
Braga, Scheila Furtado; Galvao, Douglas Soares
A structure-activity study of taxol, taxotere, and derivatives using the electronic indices methodology (EIM) Journal Article
Em: Journal of chemical information and computer sciences, vol. 43, não 2, pp. 699–706, 2003.
Resumo | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Drug Design, Electronic Structure, Taxol, Taxotere, Theory of Electronic Indices
@article{braga2003structure,
title = {A structure-activity study of taxol, taxotere, and derivatives using the electronic indices methodology (EIM)},
author = {Braga, Scheila Furtado and Galvao, Douglas Soares},
url = {http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ci025640v},
year = {2003},
date = {2003-01-01},
journal = {Journal of chemical information and computer sciences},
volume = {43},
number = {2},
pages = {699--706},
publisher = {American Chemical Society},
abstract = {Among the new families of effective anticancer drugs, the natural product paclitaxel (Taxol/Bristol-MyersSquibb)
and its semisynthetic derivative docetaxel (Taxotere/Rhone-Poulenc Rorer) are probably the most
promising agents under investigation. Surprisingly considering their importance no detailed quantum
mechanical studies have been carried out for these drugs. In this work we report the first structure-activity
relationship (SAR) studies for 20 taxoid structures using molecular descriptors from all-electron quantum
methods. The used methods were the pattern-recognition Principal Component Analysis (PCA), Hierarchical
Clustering Analysis (HCA), and the recently developed Electronic Indices Methodology (EIM). The combined
use of EIM with PCA/HCA methodologies was able to correctly classify active and inactive taxoids with
100% of accuracy using only a few “universal” quantum molecular descriptors. It was possible to identify
the electronic features defining active molecules. This information can be used to select and design new
active compounds. The combined use of EIM with PCA/HCA can be a new and very efficient tool in the
field of computer assisted drug design.},
keywords = {Drug Design, Electronic Structure, Taxol, Taxotere, Theory of Electronic Indices},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
and its semisynthetic derivative docetaxel (Taxotere/Rhone-Poulenc Rorer) are probably the most
promising agents under investigation. Surprisingly considering their importance no detailed quantum
mechanical studies have been carried out for these drugs. In this work we report the first structure-activity
relationship (SAR) studies for 20 taxoid structures using molecular descriptors from all-electron quantum
methods. The used methods were the pattern-recognition Principal Component Analysis (PCA), Hierarchical
Clustering Analysis (HCA), and the recently developed Electronic Indices Methodology (EIM). The combined
use of EIM with PCA/HCA methodologies was able to correctly classify active and inactive taxoids with
100% of accuracy using only a few “universal” quantum molecular descriptors. It was possible to identify
the electronic features defining active molecules. This information can be used to select and design new
active compounds. The combined use of EIM with PCA/HCA can be a new and very efficient tool in the
field of computer assisted drug design.
2002
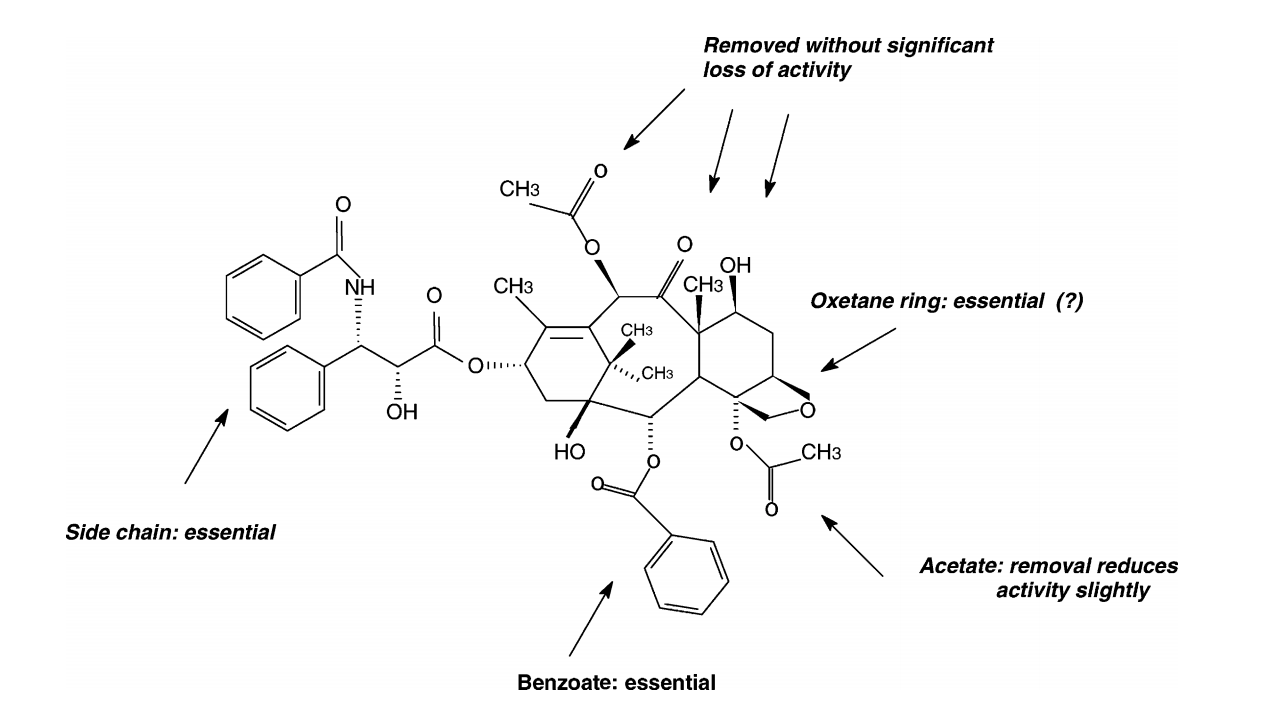
Braga, SF; Galvao, DS
A semiempirical study on the electronic structure of 10-deacetylbaccatin-III Journal Article
Em: Journal of Molecular Graphics and Modelling, vol. 21, não 1, pp. 57–70, 2002.
Resumo | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Baccatin, Drug Design, Electronic Structure, Taxol, Taxotere, Theory of Electronic Indices
@article{braga2002semiempirical,
title = {A semiempirical study on the electronic structure of 10-deacetylbaccatin-III},
author = {Braga, SF and Galvao, DS},
url = {http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1093326302001213},
year = {2002},
date = {2002-01-01},
journal = {Journal of Molecular Graphics and Modelling},
volume = {21},
number = {1},
pages = {57--70},
publisher = {Elsevier},
abstract = {We performed a conformational and electronic analysis for 10-deacetylbaccatin-III (DBAC) using well-known semiempirical methods (parametric method 3 (PM3) and Zerner’s intermediate neglect of differential overlap (ZINDO)) coupled to the concepts of total and local density of states (LDOS). Our results indicate that regions presented by paclitaxel (Taxol®) as important for the biological activity can be traced out by the electronic features present in DBAC. These molecules differ only by a phenylisoserine side chain. Compared to paclitaxel, DBAC has a simpler structure in terms of molecular size and number of degrees of freedom (d.f.). This makes DBAC a good candidate for a preliminary investigation of the taxoid family. Our results question the importance of the oxetane group, which seems to be consistent with recent experimental data.
},
keywords = {Baccatin, Drug Design, Electronic Structure, Taxol, Taxotere, Theory of Electronic Indices},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
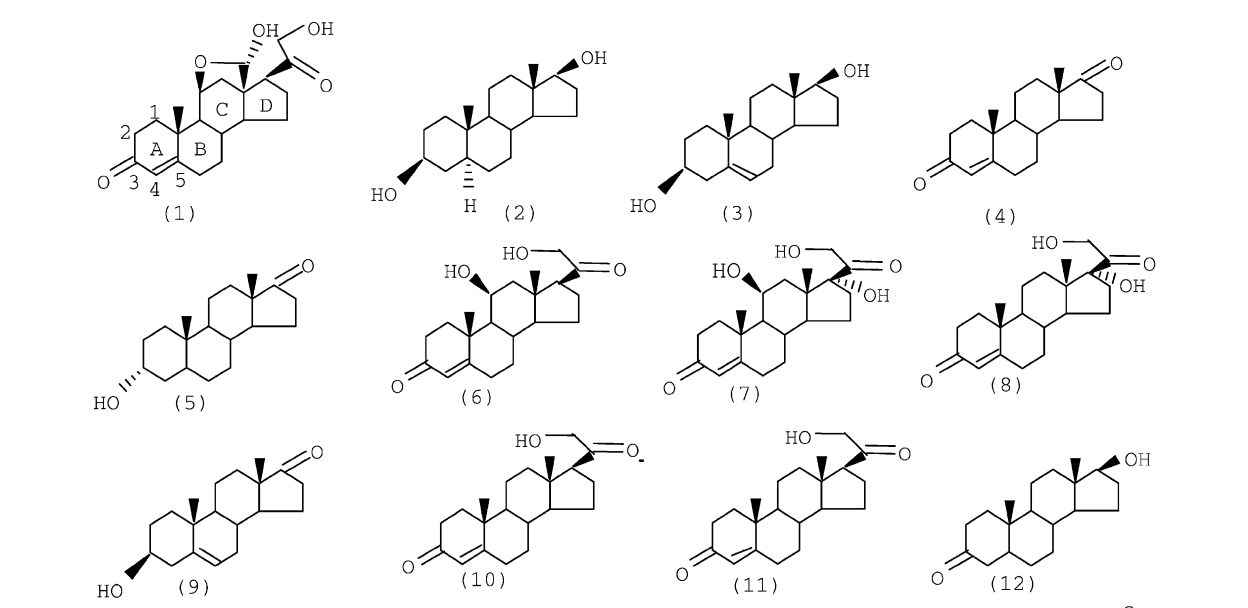
Vendrame, R; Coluci, VR; Braga, RS; Galvao, DS
Structure--activity relationship (SAR) studies of the tripos benchmark steroids Journal Article
Em: Journal of Molecular Structure: THEOCHEM, vol. 619, não 1, pp. 195–205, 2002.
Resumo | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Drug Design, Electronic Structure, HCA/PCA, Neural Networks, Tripos
@article{vendrame2002structure,
title = {Structure--activity relationship (SAR) studies of the tripos benchmark steroids},
author = {Vendrame, R and Coluci, VR and Braga, RS and Galvao, DS},
url = {http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S016612800200578X},
year = {2002},
date = {2002-01-01},
journal = {Journal of Molecular Structure: THEOCHEM},
volume = {619},
number = {1},
pages = {195--205},
publisher = {Elsevier},
abstract = {We report here qualitative structure–activity relationship (SAR) studies for the molecular set called Tripos or Cramer steroid data set. These compounds are known to bind to corticosteroid binding globulin (CBG). In the present work we have used the electronic indices methodology (EIM). The EIM is based on Boolean relational rules exploring the concepts of local density of states and critical values for energy separation involving frontier orbitals. We have also carried out comparative principal component analysis (PCA) and hierarchical clustering analysis (HCA) studies with molecular descriptors obtained from EIM calculations. EIM, PCA and HCA correctly predict (100% accuracy) the steroid's biological activity. The present studies reinforce the universal applicability of the EIM descriptors and show that the combined use of EIM coupled to PCA can be a new efficient and powerful SAR tool.
},
keywords = {Drug Design, Electronic Structure, HCA/PCA, Neural Networks, Tripos},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}


