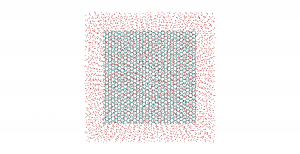
[PUBLICADO] In this work we use a three-dimensional Pauli master equation to investigate the charge carrier mobility of a two-phase system, which can mimic donor-acceptor and amorphous- crystalline bulk heterojunctions. Our approach can be separated into two parts: the morphology generation and the charge transport modeling in the generated blend. The morphology part is based …
Category: Artigos
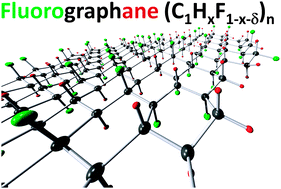
Graphynes: how they are hydrogenated
Graphyne is a generic name for a carbon allotrope family of 2D structures, where acetylenic groups connect benzenoid rings, with the coexistence of sp and sp2 hybridized carbon atoms. In this work we have investigated, through fully atomistic reactive molecular dynamics simulations, the dynamics and structural changes of the hydrogenation of α, β, and …
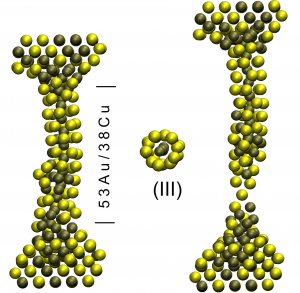
Surface effects on the mechanical elongation of AuCu nanowires: De-alloying and the formation of mixed suspended atomic chains
Lagos, MJ; Autreto, PAS; Bettini,; Sato,; Dantas, SO; Galvao, DS; Ugarte, Surface effects on the mechanical elongation of AuCu nanowires: De-alloying and the formation of mixed suspended atomic chains (Journal Article) Journal of Applied Physics, 117 (9), pp. 094301, 2015. We report here an atomistic study of the mechanical deformation of Au x Cu (1− x ) atomic-size wires …
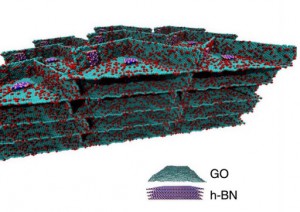
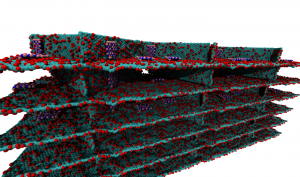
Reinforced 3D nanostructures
PUBLISHED: Nature communications, 5 2014 Low-density nanostructured foams are often limited in applications due to their low mechanical and thermal stabilities. Here we report an approach of building the structural units of three-dimensional (3D) foams using hybrid two-dimensional (2D) atomic layers made of stacked graphene oxide layers reinforced with conformal hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) platelets. The ultra-low density …
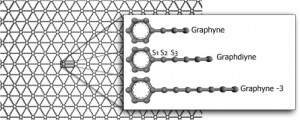
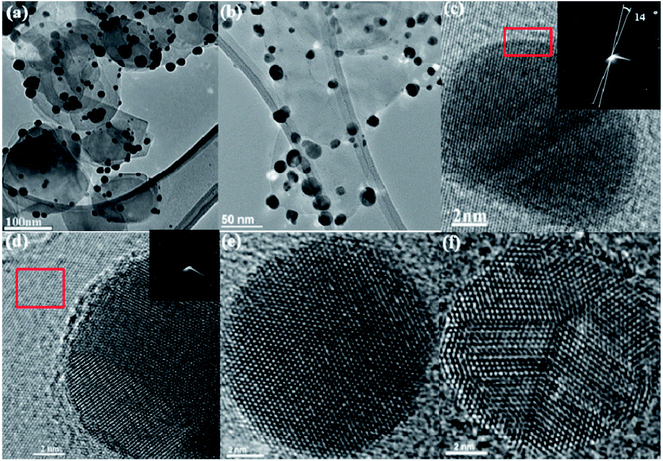
Curious hydrogenation pattern in graphdiynes
PUBLISHED: Carbon, 77 pp. 829–834, 2014. Graphene is one of the most important materials in science today due to its unique and remarkable electronic, thermal and mechanical properties. However in its pristine state, graphene is a gapless semiconductor, what limits its use in transistor electronics. In part due to the revolution created by graphene in materials science, there …
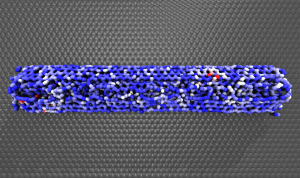
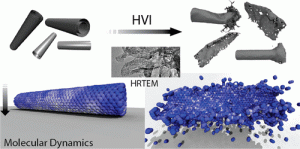
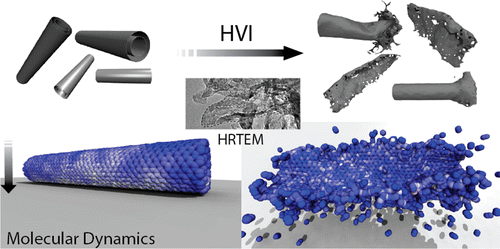
A new way to unzip carbon nanotubes
PUBLISHED: Nano letters, 14 (7), pp. 4131–4137, 2014. The way nanostructures behave and mechanically respond to high impact collision is a topic of intrigue. For anisotropic nanostructures, such as carbon nanotubes, this response will be complicated based on the impact geometry. Here we report the result of hypervelocity impact of nanotubes against solid targets and show that impact …




Comentários