Eric Perim, Douglas S. Galvao
Novel Nanoscroll Structures from Carbon Nitride Layers Online
2015, (ArXiv Draft MRS Proceedings, 1726, mrsf14-1726-j05-02 (2015)).
@online{Perim2015,
title = {Novel Nanoscroll Structures from Carbon Nitride Layers},
author = {Eric Perim, Douglas S. Galvao},
url = {http://arxiv.org/abs/1502.00260},
year = {2015},
date = {2015-02-02},
abstract = {Nanoscrolls consist of sheets rolled up into a papyrus-like form. Their open ends produce great radial flexibility, which can be exploited for a large variety of applications, from actuators to hydrogen storage. They have been successfully synthesized from different materials, including carbon and boron nitride. In this work we have investigated, through fully atomistic molecular dynamics simulations, the dynamics of scroll formation for a series of graphene-like carbon nitride (CN) two-dimensional systems: g-CN, triazine-based (g-C3N4), and heptazine-based (g-C3N4). Carbon nitride (CN) structures have been attracting great attention since their prediction as super hard materials. Recently, graphene-like carbon nitride (g-CN) structures have been synthesized with distinct stoichiometry and morphologies. By combining these unique CN characteristics with the structural properties inherent to nanoscrolls new nanostructures with very attractive mechanical and electronic properties could be formed. Our results show that stable nanoscrolls can be formed for all of CN structures we have investigated here. As the CN sheets have been already synthesized, these new scrolled structures are perfectly feasible and within our present-day technology.},
note = {ArXiv Draft MRS Proceedings, 1726, mrsf14-1726-j05-02 (2015)},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {online}
}
Eric Perim, Douglas S. Galvao
Novel Nanoscroll Structures from Carbon Nitride Layers Proceedings
vol. 1726, no. mrsf14-1726-j05-02, 2015, (MRS Proceedings, 1726, mrsf14-1726-j05-02 ).
@proceedings{Perim2015b,
title = {Novel Nanoscroll Structures from Carbon Nitride Layers},
author = {Eric Perim, Douglas S. Galvao},
url = {http://journals.cambridge.org/action/displayAbstract?fromPage=online&aid=9700860&fileId=S1946427415004650},
doi = {DOI: 10.1557/opl.2015.465},
year = {2015},
date = {2015-01-01},
volume = {1726},
number = {mrsf14-1726-j05-02},
abstract = {Nanoscrolls consist of sheets rolled up into a papyrus-like form. Their open ends produce great radial flexibility, which can be exploited for a large variety of applications, from actuators to hydrogen storage. They have been successfully synthesized from different materials, including carbon and boron nitride. In this work we have investigated, through fully atomistic molecular dynamics simulations, the dynamics of scroll formation for a series of graphene-like carbon nitride (CN) two-dimensional systems: g-CN, triazine-based (g-C3N4), and heptazine-based (g-C3N4). Carbon nitride (CN) structures have been attracting great attention since their prediction as super hard materials. Recently, graphene-like carbon nitride (g-CN) structures have been synthesized with distinct stoichiometry and morphologies. By combining these unique CN characteristics with the structural properties inherent to nanoscrolls new nanostructures with very attractive mechanical and electronic properties could be formed. Our results show that stable nanoscrolls can be formed for all of CN structures we have investigated here. As the CN sheets have been already synthesized, these new scrolled structures are perfectly feasible and within our present-day technology.},
note = {MRS Proceedings, 1726, mrsf14-1726-j05-02 },
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {proceedings}
}
Perim, Eric; Galvao, Douglas S
Novel Nanoscroll Structures from Carbon Nitride Layers Journal Article
In: ChemPhysChem, vol. 15, no. 11, pp. 2367–2371, 2014.
@article{perim2014novelb,
title = {Novel Nanoscroll Structures from Carbon Nitride Layers},
author = {Perim, Eric and Galvao, Douglas S},
url = {http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/cphc.201402059/full},
year = {2014},
date = {2014-01-01},
journal = {ChemPhysChem},
volume = {15},
number = {11},
pages = {2367--2371},
publisher = {WILEY-VCH Verlag},
abstract = {Nanoscrolls (papyrus-like nanostructures) are very attractive structures for a variety of applications, owing to their tunable diameter and large accessible surface area. They have been successfully synthesized from different materials. In this work, we investigate, through fully atomistic molecular dynamics simulations, the dynamics of scroll formation for a series of graphene-like carbon nitride (CN) two-dimensional systems: g-CN, triazine-based g-C3N4, and heptazine-based g-C3N4. Our results show that stable nanoscrolls can be formed for each of these structures. Possible synthetic routes to produce these nanostructures are also addressed.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2015
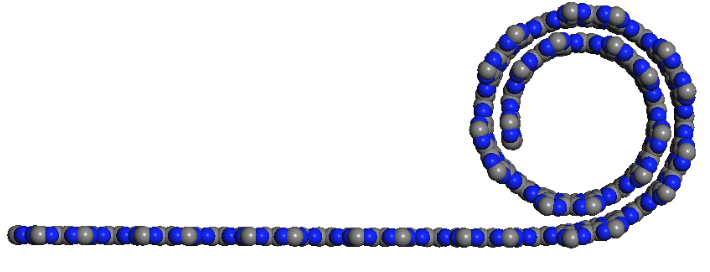
Eric Perim, Douglas S. Galvao
Novel Nanoscroll Structures from Carbon Nitride Layers Online
2015, (ArXiv Draft MRS Proceedings, 1726, mrsf14-1726-j05-02 (2015)).
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: carbon nitride, Molecular Dynamics, Scrolls
@online{Perim2015,
title = {Novel Nanoscroll Structures from Carbon Nitride Layers},
author = {Eric Perim, Douglas S. Galvao},
url = {http://arxiv.org/abs/1502.00260},
year = {2015},
date = {2015-02-02},
abstract = {Nanoscrolls consist of sheets rolled up into a papyrus-like form. Their open ends produce great radial flexibility, which can be exploited for a large variety of applications, from actuators to hydrogen storage. They have been successfully synthesized from different materials, including carbon and boron nitride. In this work we have investigated, through fully atomistic molecular dynamics simulations, the dynamics of scroll formation for a series of graphene-like carbon nitride (CN) two-dimensional systems: g-CN, triazine-based (g-C3N4), and heptazine-based (g-C3N4). Carbon nitride (CN) structures have been attracting great attention since their prediction as super hard materials. Recently, graphene-like carbon nitride (g-CN) structures have been synthesized with distinct stoichiometry and morphologies. By combining these unique CN characteristics with the structural properties inherent to nanoscrolls new nanostructures with very attractive mechanical and electronic properties could be formed. Our results show that stable nanoscrolls can be formed for all of CN structures we have investigated here. As the CN sheets have been already synthesized, these new scrolled structures are perfectly feasible and within our present-day technology.},
note = {ArXiv Draft MRS Proceedings, 1726, mrsf14-1726-j05-02 (2015)},
keywords = {carbon nitride, Molecular Dynamics, Scrolls},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {online}
}
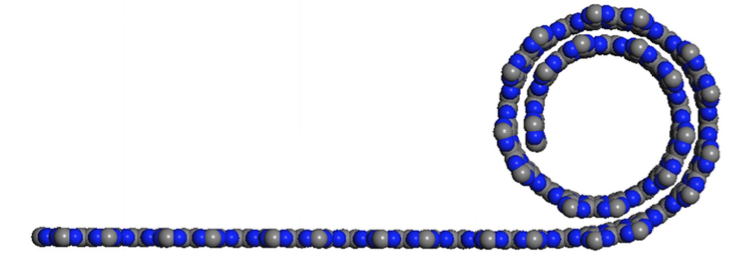
Eric Perim, Douglas S. Galvao
Novel Nanoscroll Structures from Carbon Nitride Layers Proceedings
vol. 1726, no. mrsf14-1726-j05-02, 2015, (MRS Proceedings, 1726, mrsf14-1726-j05-02 ).
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: carbon nitride, Molecular Dynamics, nanoscrolls
@proceedings{Perim2015b,
title = {Novel Nanoscroll Structures from Carbon Nitride Layers},
author = {Eric Perim, Douglas S. Galvao},
url = {http://journals.cambridge.org/action/displayAbstract?fromPage=online&aid=9700860&fileId=S1946427415004650},
doi = {DOI: 10.1557/opl.2015.465},
year = {2015},
date = {2015-01-01},
volume = {1726},
number = {mrsf14-1726-j05-02},
abstract = {Nanoscrolls consist of sheets rolled up into a papyrus-like form. Their open ends produce great radial flexibility, which can be exploited for a large variety of applications, from actuators to hydrogen storage. They have been successfully synthesized from different materials, including carbon and boron nitride. In this work we have investigated, through fully atomistic molecular dynamics simulations, the dynamics of scroll formation for a series of graphene-like carbon nitride (CN) two-dimensional systems: g-CN, triazine-based (g-C3N4), and heptazine-based (g-C3N4). Carbon nitride (CN) structures have been attracting great attention since their prediction as super hard materials. Recently, graphene-like carbon nitride (g-CN) structures have been synthesized with distinct stoichiometry and morphologies. By combining these unique CN characteristics with the structural properties inherent to nanoscrolls new nanostructures with very attractive mechanical and electronic properties could be formed. Our results show that stable nanoscrolls can be formed for all of CN structures we have investigated here. As the CN sheets have been already synthesized, these new scrolled structures are perfectly feasible and within our present-day technology.},
note = {MRS Proceedings, 1726, mrsf14-1726-j05-02 },
keywords = {carbon nitride, Molecular Dynamics, nanoscrolls},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {proceedings}
}
2014
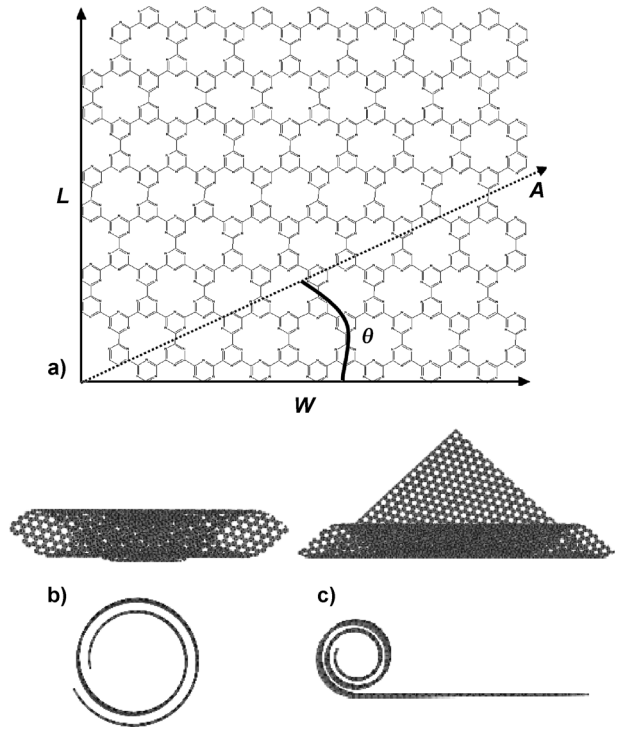
Perim, Eric; Galvao, Douglas S
Novel Nanoscroll Structures from Carbon Nitride Layers Journal Article
In: ChemPhysChem, vol. 15, no. 11, pp. 2367–2371, 2014.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: carbon nitride, Molecular Dynamics, Scrolls
@article{perim2014novelb,
title = {Novel Nanoscroll Structures from Carbon Nitride Layers},
author = {Perim, Eric and Galvao, Douglas S},
url = {http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/cphc.201402059/full},
year = {2014},
date = {2014-01-01},
journal = {ChemPhysChem},
volume = {15},
number = {11},
pages = {2367--2371},
publisher = {WILEY-VCH Verlag},
abstract = {Nanoscrolls (papyrus-like nanostructures) are very attractive structures for a variety of applications, owing to their tunable diameter and large accessible surface area. They have been successfully synthesized from different materials. In this work, we investigate, through fully atomistic molecular dynamics simulations, the dynamics of scroll formation for a series of graphene-like carbon nitride (CN) two-dimensional systems: g-CN, triazine-based g-C3N4, and heptazine-based g-C3N4. Our results show that stable nanoscrolls can be formed for each of these structures. Possible synthetic routes to produce these nanostructures are also addressed.},
keywords = {carbon nitride, Molecular Dynamics, Scrolls},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
http://scholar.google.com/citations?hl=en&user=95SvbM8AAAAJ


