Kabbani, Mohamad A.; Kochat, Vidya; Bhowmick, Sanjit; Soto, Matias; Som, Anirban; Krishnadas, K. R.; Woellner, Cristiano F.; Jaques, Ygor M.; Barrera, Enrique V.; Asif, Syed; Vajtai, Robert; Pradeep, Thalappil; Galvão, Douglas S.; Kabbani, Ahmad T.; Tiwary, Chandra Sekhar; Ajayan, Pulickel M.
Consolidation of Functionalized Graphene at Ambient Temperature via Mechano-chemistry Journal Article
In: Carbon, vol. 134, no. 8, pp. 491-499, 2018.
@article{Kabbani2018,
title = {Consolidation of Functionalized Graphene at Ambient Temperature via Mechano-chemistry},
author = {Mohamad A. Kabbani and Vidya Kochat and Sanjit Bhowmick and Matias Soto and Anirban Som and K.R. Krishnadas and Cristiano F. Woellner and Ygor M. Jaques and Enrique V. Barrera and Syed Asif and Robert Vajtai and Thalappil Pradeep and Douglas S. Galvão and Ahmad T. Kabbani and Chandra Sekhar Tiwary and Pulickel M. Ajayan},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0008622318302987?dgcid=raven_sd_aip_email},
doi = {DOI:10.1016/j.carbon.2018.03.049},
year = {2018},
date = {2018-03-22},
journal = {Carbon},
volume = {134},
number = {8},
pages = {491-499},
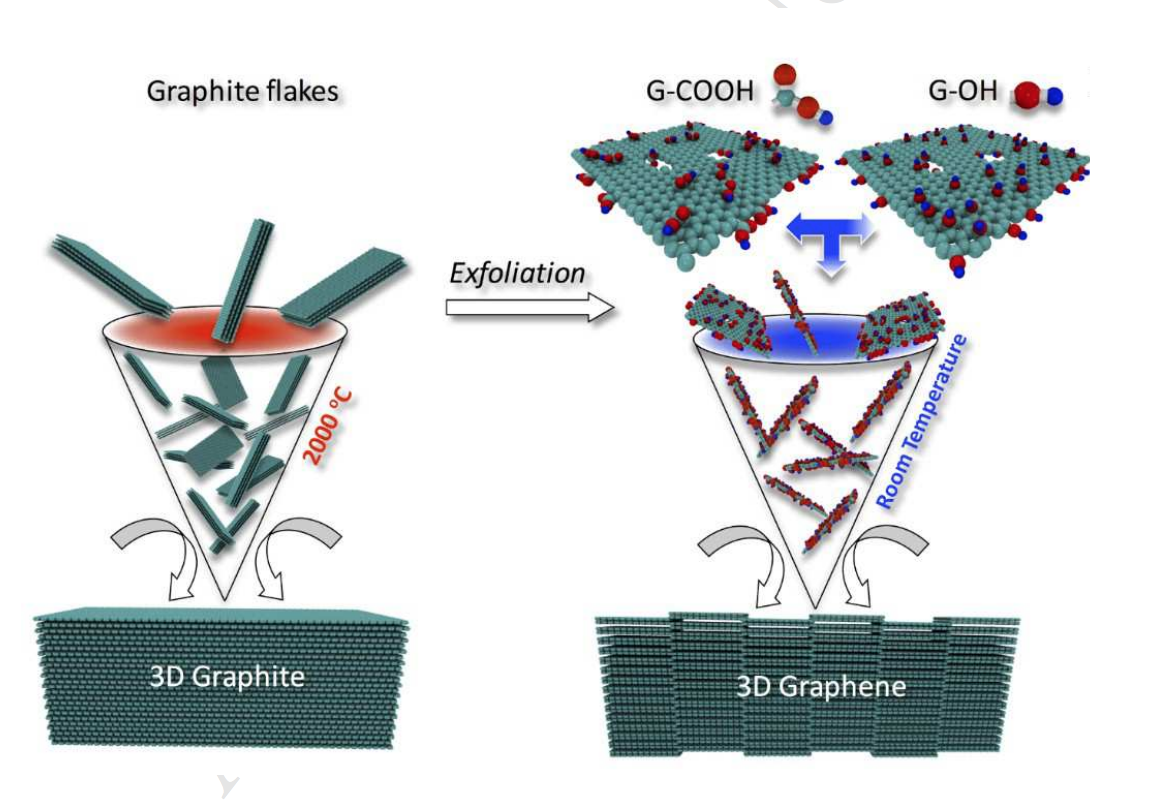
abstract = {Graphitic solids are typically produced via high temperature and energy consuming
processing (e.g. sintering) of carbon particles. Here, we demonstrate the mechano-chemical
assembly of functionalized graphene layers into 3D graphitic solids via room temperature and
low energy consuming processing. The chemical functional groups on graphene layers are
interconnected at room temperature under pressure leading to porous three-dimensional
structures with tunable mechanical and electrical properties. The formation of mechanochemistry
induced atomic scale junctions and their impact on mechanical properties of
graphene assembled carbon materials are demonstrated through nano-indentation experiments
and confirmed using DFT and molecular dynamics simulations. The results show room
temperature consolidation routes of graphene layers into bulk carbon solids.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
processing (e.g. sintering) of carbon particles. Here, we demonstrate the mechano-chemical
assembly of functionalized graphene layers into 3D graphitic solids via room temperature and
low energy consuming processing. The chemical functional groups on graphene layers are
interconnected at room temperature under pressure leading to porous three-dimensional
structures with tunable mechanical and electrical properties. The formation of mechanochemistry
induced atomic scale junctions and their impact on mechanical properties of
graphene assembled carbon materials are demonstrated through nano-indentation experiments
and confirmed using DFT and molecular dynamics simulations. The results show room
temperature consolidation routes of graphene layers into bulk carbon solids.
2018
Kabbani, Mohamad A.; Kochat, Vidya; Bhowmick, Sanjit; Soto, Matias; Som, Anirban; Krishnadas, K. R.; Woellner, Cristiano F.; Jaques, Ygor M.; Barrera, Enrique V.; Asif, Syed; Vajtai, Robert; Pradeep, Thalappil; Galvão, Douglas S.; Kabbani, Ahmad T.; Tiwary, Chandra Sekhar; Ajayan, Pulickel M.
Consolidation of Functionalized Graphene at Ambient Temperature via Mechano-chemistry Journal Article
In: Carbon, vol. 134, no. 8, pp. 491-499, 2018.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: DFT, Graphene, Mechanochemistry, Molecular Dynamics
@article{Kabbani2018,
title = {Consolidation of Functionalized Graphene at Ambient Temperature via Mechano-chemistry},
author = {Mohamad A. Kabbani and Vidya Kochat and Sanjit Bhowmick and Matias Soto and Anirban Som and K.R. Krishnadas and Cristiano F. Woellner and Ygor M. Jaques and Enrique V. Barrera and Syed Asif and Robert Vajtai and Thalappil Pradeep and Douglas S. Galvão and Ahmad T. Kabbani and Chandra Sekhar Tiwary and Pulickel M. Ajayan},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0008622318302987?dgcid=raven_sd_aip_email},
doi = {DOI:10.1016/j.carbon.2018.03.049},
year = {2018},
date = {2018-03-22},
journal = {Carbon},
volume = {134},
number = {8},
pages = {491-499},
abstract = {Graphitic solids are typically produced via high temperature and energy consuming
processing (e.g. sintering) of carbon particles. Here, we demonstrate the mechano-chemical
assembly of functionalized graphene layers into 3D graphitic solids via room temperature and
low energy consuming processing. The chemical functional groups on graphene layers are
interconnected at room temperature under pressure leading to porous three-dimensional
structures with tunable mechanical and electrical properties. The formation of mechanochemistry
induced atomic scale junctions and their impact on mechanical properties of
graphene assembled carbon materials are demonstrated through nano-indentation experiments
and confirmed using DFT and molecular dynamics simulations. The results show room
temperature consolidation routes of graphene layers into bulk carbon solids.},
keywords = {DFT, Graphene, Mechanochemistry, Molecular Dynamics},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
processing (e.g. sintering) of carbon particles. Here, we demonstrate the mechano-chemical
assembly of functionalized graphene layers into 3D graphitic solids via room temperature and
low energy consuming processing. The chemical functional groups on graphene layers are
interconnected at room temperature under pressure leading to porous three-dimensional
structures with tunable mechanical and electrical properties. The formation of mechanochemistry
induced atomic scale junctions and their impact on mechanical properties of
graphene assembled carbon materials are demonstrated through nano-indentation experiments
and confirmed using DFT and molecular dynamics simulations. The results show room
temperature consolidation routes of graphene layers into bulk carbon solids.
http://scholar.google.com/citations?hl=en&user=95SvbM8AAAAJ


