Oliveira, Eliezer Fernando; Santos, Ricardo Paupitz; da Silva Autreto, Pedro Alves; Stanislav Moshkalev,; Galvao, Douglas Soares
Improving Graphene-metal Contacts: Thermal Induced Polishing Online
2018, (preprint ArXiv:1801.04785).
@online{Oliveira2018d,
title = {Improving Graphene-metal Contacts: Thermal Induced Polishing},
author = {Eliezer Fernando Oliveira and Ricardo Paupitz Santos and Pedro Alves da Silva Autreto and Stanislav Moshkalev, and Douglas Soares Galvao},
url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/1801.04785},
year = {2018},
date = {2018-01-15},
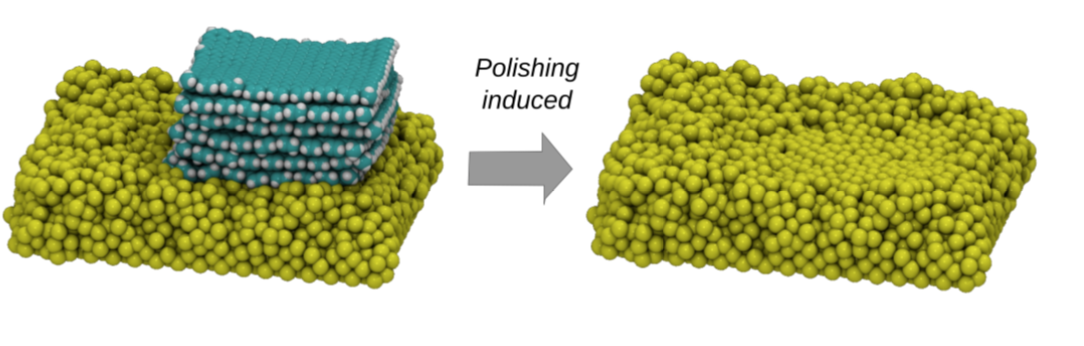
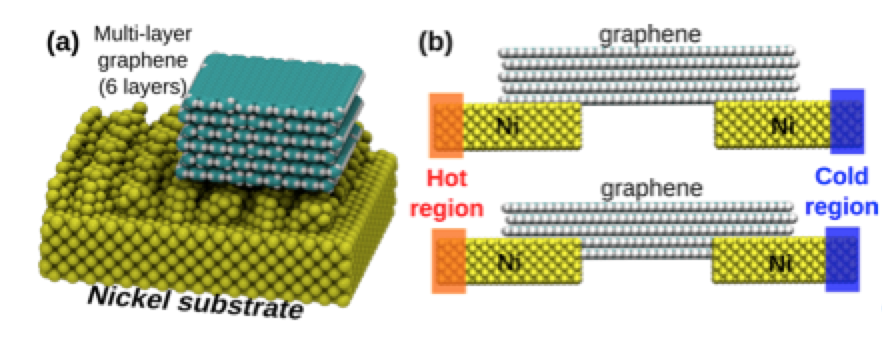
abstract = {Graphene is a very promising material for nanoelectronics applications due to its unique and remarkable electronic and thermal properties. However, when deposited on metallic electrodes the overall thermal conductivity is significantly decreased. This phenomenon has been attributed to the mismatch between the interfaces and contact thermal resistance. Experimentally, one way to improve the graphene/metal contact is thorough high-temperature annealing, but the detailed mechanisms behind these processes remain unclear. In order to address these questions, we carried out fully atomistic reactive molecular dynamics simulations using the ReaxFF force field to investigate the interactions between multi-layer graphene and metallic electrodes (nickel) under (thermal) annealing. Our results show that the annealing induces an upward-downward movement of the graphene layers, causing a pile- driver-like effect over the metallic surface. This graphene induced movements cause a planarization (thermal polishing-like effect) of the metallic surface, which results in the increase of the effective graphene/metal contact area. This can also explain the experimentally observed improvements of the thermal and electric conductivities.},
note = {preprint ArXiv:1801.04785},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {online}
}
Oliveira, Eliezer Fernando; Paupitz, Ricardo; da Silva Autreto, Pedro Alves; Moshkalev, Stanislav; Galvao, Douglas Soares
Improving Graphene-metal Contacts: Thermal Induced Polishing Journal Article
In: MRS Advances, vol. 3, no. 1-2, pp. 73-78, 2018.
@article{Oliveira2018c,
title = {Improving Graphene-metal Contacts: Thermal Induced Polishing },
author = {Eliezer Fernando Oliveira and Ricardo Paupitz and Pedro Alves da Silva Autreto and Stanislav Moshkalev and Douglas Soares Galvao},
url = {https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/mrs-advances/article/improving-graphenemetal-contacts-thermal-induced-polishing/AC01C4996B90B0EE5E03220604071D12},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1557/adv.2018.66},
year = {2018},
date = {2018-01-01},
journal = {MRS Advances},
volume = {3},
number = {1-2},
pages = {73-78},
abstract = {Graphene is a very promising material for nanoelectronics applications due to its unique and remarkable electronic and thermal properties. However, when deposited on metallic electrodes the overall thermal conductivity is significantly decreased. This phenomenon has been attributed to the mismatch between the interfaces and contact thermal resistance. Experimentally, one way to improve the graphene/metal contact is thorough high-temperature annealing, but the detailed mechanisms behind these processes remain unclear. In order to address these questions, we carried out fully atomistic reactive molecular dynamics simulations using the ReaxFF force field to investigate the interactions between multi-layer graphene and metallic electrodes (nickel) under (thermal) annealing. Our results show that the annealing induces an upward-downward movement of the graphene layers, causing a pile-driver-like effect over the metallic surface. This graphene induced movements cause a planarization (thermal polishing-like effect) of the metallic surface, which results in the increase of the effective graphene/metal contact area. This can also explain the experimentally observed improvements of the thermal and electric conductivities.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2018
Oliveira, Eliezer Fernando; Santos, Ricardo Paupitz; da Silva Autreto, Pedro Alves; Stanislav Moshkalev,; Galvao, Douglas Soares
Improving Graphene-metal Contacts: Thermal Induced Polishing Online
2018, (preprint ArXiv:1801.04785).
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: contacts, Graphene, Molecular Dynamics, thermal properties
@online{Oliveira2018d,
title = {Improving Graphene-metal Contacts: Thermal Induced Polishing},
author = {Eliezer Fernando Oliveira and Ricardo Paupitz Santos and Pedro Alves da Silva Autreto and Stanislav Moshkalev, and Douglas Soares Galvao},
url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/1801.04785},
year = {2018},
date = {2018-01-15},
abstract = {Graphene is a very promising material for nanoelectronics applications due to its unique and remarkable electronic and thermal properties. However, when deposited on metallic electrodes the overall thermal conductivity is significantly decreased. This phenomenon has been attributed to the mismatch between the interfaces and contact thermal resistance. Experimentally, one way to improve the graphene/metal contact is thorough high-temperature annealing, but the detailed mechanisms behind these processes remain unclear. In order to address these questions, we carried out fully atomistic reactive molecular dynamics simulations using the ReaxFF force field to investigate the interactions between multi-layer graphene and metallic electrodes (nickel) under (thermal) annealing. Our results show that the annealing induces an upward-downward movement of the graphene layers, causing a pile- driver-like effect over the metallic surface. This graphene induced movements cause a planarization (thermal polishing-like effect) of the metallic surface, which results in the increase of the effective graphene/metal contact area. This can also explain the experimentally observed improvements of the thermal and electric conductivities.},
note = {preprint ArXiv:1801.04785},
keywords = {contacts, Graphene, Molecular Dynamics, thermal properties},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {online}
}
Oliveira, Eliezer Fernando; Paupitz, Ricardo; da Silva Autreto, Pedro Alves; Moshkalev, Stanislav; Galvao, Douglas Soares
Improving Graphene-metal Contacts: Thermal Induced Polishing Journal Article
In: MRS Advances, vol. 3, no. 1-2, pp. 73-78, 2018.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: contacts, Graphene, Molecular Dynamics, thermal properties
@article{Oliveira2018c,
title = {Improving Graphene-metal Contacts: Thermal Induced Polishing },
author = {Eliezer Fernando Oliveira and Ricardo Paupitz and Pedro Alves da Silva Autreto and Stanislav Moshkalev and Douglas Soares Galvao},
url = {https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/mrs-advances/article/improving-graphenemetal-contacts-thermal-induced-polishing/AC01C4996B90B0EE5E03220604071D12},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1557/adv.2018.66},
year = {2018},
date = {2018-01-01},
journal = {MRS Advances},
volume = {3},
number = {1-2},
pages = {73-78},
abstract = {Graphene is a very promising material for nanoelectronics applications due to its unique and remarkable electronic and thermal properties. However, when deposited on metallic electrodes the overall thermal conductivity is significantly decreased. This phenomenon has been attributed to the mismatch between the interfaces and contact thermal resistance. Experimentally, one way to improve the graphene/metal contact is thorough high-temperature annealing, but the detailed mechanisms behind these processes remain unclear. In order to address these questions, we carried out fully atomistic reactive molecular dynamics simulations using the ReaxFF force field to investigate the interactions between multi-layer graphene and metallic electrodes (nickel) under (thermal) annealing. Our results show that the annealing induces an upward-downward movement of the graphene layers, causing a pile-driver-like effect over the metallic surface. This graphene induced movements cause a planarization (thermal polishing-like effect) of the metallic surface, which results in the increase of the effective graphene/metal contact area. This can also explain the experimentally observed improvements of the thermal and electric conductivities.},
keywords = {contacts, Graphene, Molecular Dynamics, thermal properties},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
http://scholar.google.com/citations?hl=en&user=95SvbM8AAAAJ


