Sajadi, Seyed Mohammad; Owuor, Peter Samora; Schara, Steven; Woellner, Cristiano F.; Rodrigues, Varlei; Vajtai, Robert; Lou, Jun; Galvao, Douglas S.; Tiwary, Chandra Sekhar; Ajayan, Pulickel M.
Multi-scale Geometric Design Principles Applied to 3D Printed Schwartizes Journal Article
In: Advanced Materials, vol. 2017, pp. 1704820, 2017.
@article{Sajadi2017,
title = {Multi-scale Geometric Design Principles Applied to 3D Printed Schwartizes},
author = {Seyed Mohammad Sajadi and Peter Samora Owuor and Steven Schara and Cristiano F. Woellner and Varlei Rodrigues and Robert Vajtai and Jun Lou and Douglas S. Galvao and Chandra Sekhar Tiwary and Pulickel M. Ajayan},
url = {http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.201704820/full},
doi = {10.1002/adma.201704820},
year = {2017},
date = {2017-09-14},
journal = {Advanced Materials},
volume = {2017},
pages = {1704820},
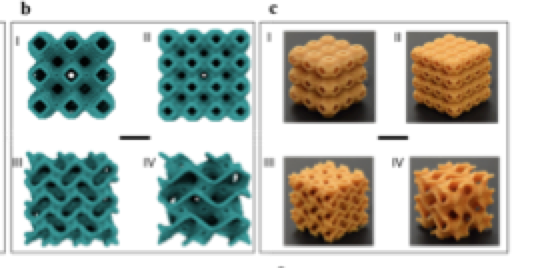
abstract = {Schwartzites are 3D porous solids with periodic minimal surfaces having negative Gaussian curvatures and can possess unusual mechanical and electronic properties. The mechanical behavior of primitive and gyroid schwartzite structures across different length scales is investigated after these geometries are 3D printed at centimeter length scales based on molec- ular models. Molecular dynamics and nite elements simulations are used
to gain further understanding on responses of these complex solids under compressive loads and kinetic impact experiments. The results show that these structures hold great promise as high load bearing and impact-resistant materials due to a unique layered deformation mechanism that emerges in these architectures during loading. Easily scalable techniques such as 3D printing can be used for exploring mechanical behavior of various predicted complex geometrical shapes to build innovative engineered materials with tunable properties.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
to gain further understanding on responses of these complex solids under compressive loads and kinetic impact experiments. The results show that these structures hold great promise as high load bearing and impact-resistant materials due to a unique layered deformation mechanism that emerges in these architectures during loading. Easily scalable techniques such as 3D printing can be used for exploring mechanical behavior of various predicted complex geometrical shapes to build innovative engineered materials with tunable properties.
2017
Sajadi, Seyed Mohammad; Owuor, Peter Samora; Schara, Steven; Woellner, Cristiano F.; Rodrigues, Varlei; Vajtai, Robert; Lou, Jun; Galvao, Douglas S.; Tiwary, Chandra Sekhar; Ajayan, Pulickel M.
Multi-scale Geometric Design Principles Applied to 3D Printed Schwartizes Journal Article
In: Advanced Materials, vol. 2017, pp. 1704820, 2017.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: 3D printing, Mechanical Properties, Molecular Dynamics, Schwarzites
@article{Sajadi2017,
title = {Multi-scale Geometric Design Principles Applied to 3D Printed Schwartizes},
author = {Seyed Mohammad Sajadi and Peter Samora Owuor and Steven Schara and Cristiano F. Woellner and Varlei Rodrigues and Robert Vajtai and Jun Lou and Douglas S. Galvao and Chandra Sekhar Tiwary and Pulickel M. Ajayan},
url = {http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.201704820/full},
doi = {10.1002/adma.201704820},
year = {2017},
date = {2017-09-14},
journal = {Advanced Materials},
volume = {2017},
pages = {1704820},
abstract = {Schwartzites are 3D porous solids with periodic minimal surfaces having negative Gaussian curvatures and can possess unusual mechanical and electronic properties. The mechanical behavior of primitive and gyroid schwartzite structures across different length scales is investigated after these geometries are 3D printed at centimeter length scales based on molec- ular models. Molecular dynamics and nite elements simulations are used
to gain further understanding on responses of these complex solids under compressive loads and kinetic impact experiments. The results show that these structures hold great promise as high load bearing and impact-resistant materials due to a unique layered deformation mechanism that emerges in these architectures during loading. Easily scalable techniques such as 3D printing can be used for exploring mechanical behavior of various predicted complex geometrical shapes to build innovative engineered materials with tunable properties.},
keywords = {3D printing, Mechanical Properties, Molecular Dynamics, Schwarzites},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
to gain further understanding on responses of these complex solids under compressive loads and kinetic impact experiments. The results show that these structures hold great promise as high load bearing and impact-resistant materials due to a unique layered deformation mechanism that emerges in these architectures during loading. Easily scalable techniques such as 3D printing can be used for exploring mechanical behavior of various predicted complex geometrical shapes to build innovative engineered materials with tunable properties.
http://scholar.google.com/citations?hl=en&user=95SvbM8AAAAJ


