Gustavo Brunetto Sehmus Ozden, N. S. Karthiselva
Controlled 3D Carbon Nanotube Structures by Plasma Welding Journal Article
In: Advanced Materials Interfaces, vol. 2016, pp. 1500755, 2016.
@article{Ozden2016,
title = {Controlled 3D Carbon Nanotube Structures by Plasma Welding},
author = {Sehmus Ozden, Gustavo Brunetto, N. S. Karthiselva, Douglas S. Galvão, Ajit Roy, Srinivasa R. Bakshi, Chandra S. Tiwary, andPulickel M. Ajayan},
url = {http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/admi.201500755/abstract?campaign=wolearlyview},
doi = {10.1002/admi.201500755},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-03-17},
journal = {Advanced Materials Interfaces},
volume = {2016},
pages = {1500755},
abstract = {3D interconnected carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are synthesized using an industrially scalable spark plasma technique. At high electric field and elevated temperature under sufficient stress the nanotubes are welded together to form a solid block. The detailed spectroscopic and microscopic analyses show successful welding of the CNTs and formation of interconnected networks. The mechanical characteristics of the 3D CNT block show a high stiffness and yield strength. A full atomistic molecular dynamics simulation elucidates the CNT welding mechanism.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Fonseca, AD; Malta, CP; Galvao, DS
Elastic Properties of Normal and Binormal Helical Nanowires Proceedings
Warrendale, Pa.; Materials Research Society; 1999, vol. 963, 2007.
@proceedings{fonseca2007elastic,
title = {Elastic Properties of Normal and Binormal Helical Nanowires},
author = {Fonseca, AD and Malta, CP and Galvao, DS},
url = {http://journals.cambridge.org/action/displayAbstract?fromPage=online&aid=8026852},
year = {2007},
date = {2007-01-01},
journal = {MATERIALS RESEARCH SOCIETY SYMPOSIUM PROCEEDINGS},
volume = {963},
pages = {88},
publisher = {Warrendale, Pa.; Materials Research Society; 1999},
abstract = {A helical nanowire can be defined as being a nanoscopic rod whose axis follows a helical curve in space. In the case of a nanowire with asymmetric cross section, the helical nanostructure can be classified as normal or binormal helix, according to the orientation of the cross section with respect to the helical axis of the structure. In this work, we present a simple model to study the elastic properties of a helical nanowire with asymmetric cross section. We use the framework of the Kirchhoff rod model to obtain an expression relating the Hooke's constant, h, of normal and binormal nanohelices to their geometric features. We also obtain the Young's modulus values. These relations can be used by experimentalists to evaluate the elastic properties of helical nanostructures. We showed that the Hooke's constant of a normal nanohelix is higher than that of a binormal one. We illustrate our results using experimentally obtained nanohelices reported in the literature.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {proceedings}
}
Fonseca, Alexandre F; Malta, CP; Galvao, DS
Is it possible to grow amorphous normal nanosprings? Journal Article
In: Nanotechnology, vol. 18, no. 43, pp. 435606, 2007.
@article{fonseca2007possible,
title = {Is it possible to grow amorphous normal nanosprings?},
author = {Fonseca, Alexandre F and Malta, CP and Galvao, DS},
url = {http://iopscience.iop.org/0957-4484/18/43/435606},
year = {2007},
date = {2007-01-01},
journal = {Nanotechnology},
volume = {18},
number = {43},
pages = {435606},
publisher = {IOP Publishing},
abstract = {Nanosprings have been objects of intense investigations in recent years. They can be classified as normal or binormal depending on the geometry of their cross-section. As normal amorphous nanosprings have not yet been observed experimentally, we have decided to investigate this matter. We discuss the shape of the catalyst in terms of the cross-sectional shape of the nanospring and show that, within the vapor–liquid–solid model, the growth of amorphous binormal nanosprings is energetically favored.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Pugno, Nicola; Coluci, V; Galvao, DS
Nanotube-or graphene-based nanoarmors Book Chapter
In: Computational & Experimental Analysis of Damaged Materials, pp. 145-154 , 2007.
@inbook{pugno2007nanotube,
title = {Nanotube-or graphene-based nanoarmors},
author = {Pugno, Nicola and Coluci, V and Galvao, DS},
url = {http://www.ing.unitn.it/~pugno/NP_PDF/IV/5-COLUCI07.pdf},
year = {2007},
date = {2007-01-01},
booktitle = {Computational & Experimental Analysis of Damaged Materials},
pages = {145-154 },
abstract = { In this paper, nanoimpacts on hexagonal or
crossbar nanotube networks as well as on graphene
sheets are investigated by elasticity and finite
kinematics or impact molecular dynamic simulations.
A transition from bending to stretching by increasing
the impact kinetic energy of the nanoprojectile is
clearly observed. The analysis suggests that the
investigated nanotextures are ideal for designing
futuristic nanoarmors. },
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inbook}
}
crossbar nanotube networks as well as on graphene
sheets are investigated by elasticity and finite
kinematics or impact molecular dynamic simulations.
A transition from bending to stretching by increasing
the impact kinetic energy of the nanoprojectile is
clearly observed. The analysis suggests that the
investigated nanotextures are ideal for designing
futuristic nanoarmors.
da Fonseca, Alexandre F; Malta, CP; Galvao, Douglas S
Elastic properties of nanowires Journal Article
In: Journal of Applied Physics, vol. 99, no. 9, pp. 094310, 2006.
@article{da2006elastic,
title = {Elastic properties of nanowires},
author = {da Fonseca, Alexandre F and Malta, CP and Galvao, Douglas S},
url = {http://scitation.aip.org/content/aip/journal/jap/99/9/10.1063/1.2194309},
year = {2006},
date = {2006-01-01},
journal = {Journal of Applied Physics},
volume = {99},
number = {9},
pages = {094310},
publisher = {AIP Publishing},
abstract = {We present a model to study Young’s modulus and Poisson’s ratio of the composite material of amorphous nanowires. It is an extension of the model derived by two of us [da Fonseca and Galvão, Phys. Rev. Lett.92, 175502 (2004)] to study the elastic properties of amorphous nanosprings. The model is based on twisting and tensioning a straight nanowire and we propose an experimental setup to obtain the elastic parameters of the nanowire. We used the Kirchhoff rod model to obtain the expressions for the elastic constants of the nanowire.
},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
da Fonseca, Alexandre Fontes; Malta, CP; Galvao, Douglas S
Elastic Properties of Normal and Binormal Helical Nanowires Proceedings
Cambridge University Press, vol. 963, 2006.
@proceedings{da2006elasticb,
title = {Elastic Properties of Normal and Binormal Helical Nanowires},
author = {da Fonseca, Alexandre Fontes and Malta, CP and Galvao, Douglas S},
url = {http://journals.cambridge.org/action/displayAbstract?fromPage=online&aid=8026852},
year = {2006},
date = {2006-01-01},
journal = {MRS Proceedings},
volume = {963},
pages = {0963--Q20},
publisher = {Cambridge University Press},
abstract = {A helical nanowire can be defined as being a nanoscopic rod whose axis follows a helical curve in space. In the case of a nanowire with asymmetric cross section, the helical nanostructure can be classified as normal or binormal helix, according to the orientation of the cross section with respect to the helical axis of the structure. In this work, we present a simple model to study the elastic properties of a helical nanowire with asymmetric cross section. We use the framework of the Kirchhoff rod model to obtain an expression relating the Hooke's constant, h, of normal and binormal nanohelices to their geometric features. We also obtain the Young's modulus values. These relations can be used by experimentalists to evaluate the elastic properties of helical nanostructures. We showed that the Hooke's constant of a normal nanohelix is higher than that of a binormal one. We illustrate our results using experimentally obtained nanohelices reported in the literature.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {proceedings}
}
da Fonseca, Alexandre F; Malta, CP; Galvao, DS
Mechanical properties of amorphous nanosprings Journal Article
In: Nanotechnology, vol. 17, no. 22, pp. 5620, 2006.
@article{da2006mechanical,
title = {Mechanical properties of amorphous nanosprings},
author = {da Fonseca, Alexandre F and Malta, CP and Galvao, DS},
url = {http://iopscience.iop.org/0957-4484/17/22/015},
year = {2006},
date = {2006-01-01},
journal = {Nanotechnology},
volume = {17},
number = {22},
pages = {5620},
publisher = {IOP Publishing},
abstract = {Helical amorphous nanosprings have attracted particular interest due to their special mechanical properties. In this work we present a simple model, within the framework of the Kirchhoff rod model, for investigating the structural properties of nanosprings having asymmetric cross section. We have derived expressions that can be used to obtain the Young's modulus and Poisson's ratio of the nanospring material composite. We also address the importance of the presence of a catalyst in the growth process of amorphous nanosprings in terms of the stability of helical rods.
},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
da Fonseca, Alexandre F; Galvao, Douglas S; Malta, Coraci P
Binormal nanohelices Proceedings
Cambridge University Press, vol. 903, 2005.
@proceedings{da2005binormal,
title = {Binormal nanohelices},
author = {da Fonseca, Alexandre F and Galvao, Douglas S and Malta, Coraci P},
url = {http://journals.cambridge.org/action/displayAbstract?fromPage=online&aid=8108794&fileId=S1946427400047680},
year = {2005},
date = {2005-01-01},
journal = {MRS Proceedings},
volume = {903},
pages = {0903--Z14},
publisher = {Cambridge University Press},
abstract = {Helical structures can be classified in accordance with the orientation of its cross-section with respect to the normal or binormal vectors. We investigate the geometric features of several nanosprings verifying the non-existence of normal nanohelices. In this work, using the VLS growth model, we explain not only the absence of normal nanosprings but also the growing process of binormal nanosprings. The dynamical stability of crystalline ZnO binormal nanohelices is also addressed.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {proceedings}
}
da Fonseca, Alexandre F; Galvao, Douglas S
Mechanical properties of nanosprings Journal Article
In: Physical review letters, vol. 92, no. 17, pp. 175502, 2004.
@article{da2004mechanical,
title = {Mechanical properties of nanosprings},
author = {da Fonseca, Alexandre F and Galvao, Douglas S},
url = {http://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevLett.92.175502},
year = {2004},
date = {2004-01-01},
journal = {Physical review letters},
volume = {92},
number = {17},
pages = {175502},
publisher = {APS},
abstract = {Nanostructures (nanotubes, nanowires, etc.) have been the object of intense theoretical and experimental investigations in recent years. Among these structures, helical nanosprings or nanocoils have attracted particular interest due to their special mechanical properties. In this work, we investigated structural properties of nanosprings in the Kirchhoff rod model. We derived expressions that can be used experimentally to obtain nanospring Young’s modulus and Poisson’s ratio values. Our results also might explain why the presence of catalytic particles is so important in nanostructure growth.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2016
Gustavo Brunetto Sehmus Ozden, N. S. Karthiselva
Controlled 3D Carbon Nanotube Structures by Plasma Welding Journal Article
In: Advanced Materials Interfaces, vol. 2016, pp. 1500755, 2016.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: 3D networks, Carbon Nanotubes, Elasticity, Molecular Dynamics
@article{Ozden2016,
title = {Controlled 3D Carbon Nanotube Structures by Plasma Welding},
author = {Sehmus Ozden, Gustavo Brunetto, N. S. Karthiselva, Douglas S. Galvão, Ajit Roy, Srinivasa R. Bakshi, Chandra S. Tiwary, andPulickel M. Ajayan},
url = {http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/admi.201500755/abstract?campaign=wolearlyview},
doi = {10.1002/admi.201500755},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-03-17},
journal = {Advanced Materials Interfaces},
volume = {2016},
pages = {1500755},
abstract = {3D interconnected carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are synthesized using an industrially scalable spark plasma technique. At high electric field and elevated temperature under sufficient stress the nanotubes are welded together to form a solid block. The detailed spectroscopic and microscopic analyses show successful welding of the CNTs and formation of interconnected networks. The mechanical characteristics of the 3D CNT block show a high stiffness and yield strength. A full atomistic molecular dynamics simulation elucidates the CNT welding mechanism.},
keywords = {3D networks, Carbon Nanotubes, Elasticity, Molecular Dynamics},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2007

Fonseca, AD; Malta, CP; Galvao, DS
Elastic Properties of Normal and Binormal Helical Nanowires Proceedings
Warrendale, Pa.; Materials Research Society; 1999, vol. 963, 2007.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Elasticity, Helical Structures, Mechanical Properties, Nanowires
@proceedings{fonseca2007elastic,
title = {Elastic Properties of Normal and Binormal Helical Nanowires},
author = {Fonseca, AD and Malta, CP and Galvao, DS},
url = {http://journals.cambridge.org/action/displayAbstract?fromPage=online&aid=8026852},
year = {2007},
date = {2007-01-01},
journal = {MATERIALS RESEARCH SOCIETY SYMPOSIUM PROCEEDINGS},
volume = {963},
pages = {88},
publisher = {Warrendale, Pa.; Materials Research Society; 1999},
abstract = {A helical nanowire can be defined as being a nanoscopic rod whose axis follows a helical curve in space. In the case of a nanowire with asymmetric cross section, the helical nanostructure can be classified as normal or binormal helix, according to the orientation of the cross section with respect to the helical axis of the structure. In this work, we present a simple model to study the elastic properties of a helical nanowire with asymmetric cross section. We use the framework of the Kirchhoff rod model to obtain an expression relating the Hooke's constant, h, of normal and binormal nanohelices to their geometric features. We also obtain the Young's modulus values. These relations can be used by experimentalists to evaluate the elastic properties of helical nanostructures. We showed that the Hooke's constant of a normal nanohelix is higher than that of a binormal one. We illustrate our results using experimentally obtained nanohelices reported in the literature.},
keywords = {Elasticity, Helical Structures, Mechanical Properties, Nanowires},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {proceedings}
}
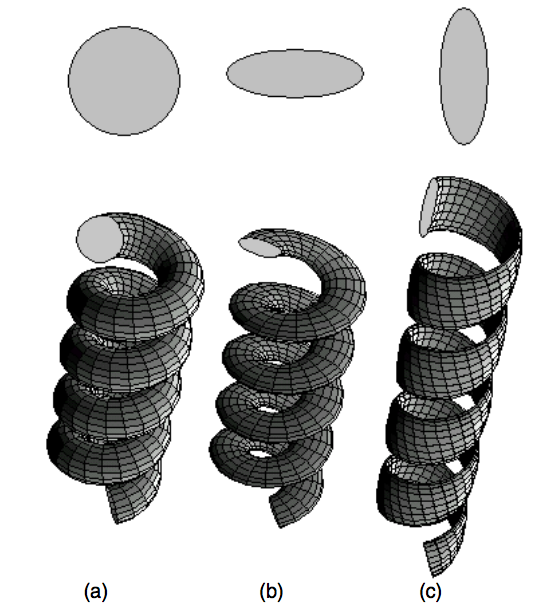
Fonseca, Alexandre F; Malta, CP; Galvao, DS
Is it possible to grow amorphous normal nanosprings? Journal Article
In: Nanotechnology, vol. 18, no. 43, pp. 435606, 2007.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Elasticity, Helical Structures, Mechanical Properties, Nanowires
@article{fonseca2007possible,
title = {Is it possible to grow amorphous normal nanosprings?},
author = {Fonseca, Alexandre F and Malta, CP and Galvao, DS},
url = {http://iopscience.iop.org/0957-4484/18/43/435606},
year = {2007},
date = {2007-01-01},
journal = {Nanotechnology},
volume = {18},
number = {43},
pages = {435606},
publisher = {IOP Publishing},
abstract = {Nanosprings have been objects of intense investigations in recent years. They can be classified as normal or binormal depending on the geometry of their cross-section. As normal amorphous nanosprings have not yet been observed experimentally, we have decided to investigate this matter. We discuss the shape of the catalyst in terms of the cross-sectional shape of the nanospring and show that, within the vapor–liquid–solid model, the growth of amorphous binormal nanosprings is energetically favored.},
keywords = {Elasticity, Helical Structures, Mechanical Properties, Nanowires},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Pugno, Nicola; Coluci, V; Galvao, DS
Nanotube-or graphene-based nanoarmors Book Chapter
In: Computational & Experimental Analysis of Damaged Materials, pp. 145-154 , 2007.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Elasticity, Mechanical Properties, Molecular Dynamics, Super Carbons
@inbook{pugno2007nanotube,
title = {Nanotube-or graphene-based nanoarmors},
author = {Pugno, Nicola and Coluci, V and Galvao, DS},
url = {http://www.ing.unitn.it/~pugno/NP_PDF/IV/5-COLUCI07.pdf},
year = {2007},
date = {2007-01-01},
booktitle = {Computational & Experimental Analysis of Damaged Materials},
pages = {145-154 },
abstract = { In this paper, nanoimpacts on hexagonal or
crossbar nanotube networks as well as on graphene
sheets are investigated by elasticity and finite
kinematics or impact molecular dynamic simulations.
A transition from bending to stretching by increasing
the impact kinetic energy of the nanoprojectile is
clearly observed. The analysis suggests that the
investigated nanotextures are ideal for designing
futuristic nanoarmors. },
keywords = {Elasticity, Mechanical Properties, Molecular Dynamics, Super Carbons},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inbook}
}
crossbar nanotube networks as well as on graphene
sheets are investigated by elasticity and finite
kinematics or impact molecular dynamic simulations.
A transition from bending to stretching by increasing
the impact kinetic energy of the nanoprojectile is
clearly observed. The analysis suggests that the
investigated nanotextures are ideal for designing
futuristic nanoarmors.
2006
da Fonseca, Alexandre F; Malta, CP; Galvao, Douglas S
Elastic properties of nanowires Journal Article
In: Journal of Applied Physics, vol. 99, no. 9, pp. 094310, 2006.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Elasticity, Filaments, Nanowires
@article{da2006elastic,
title = {Elastic properties of nanowires},
author = {da Fonseca, Alexandre F and Malta, CP and Galvao, Douglas S},
url = {http://scitation.aip.org/content/aip/journal/jap/99/9/10.1063/1.2194309},
year = {2006},
date = {2006-01-01},
journal = {Journal of Applied Physics},
volume = {99},
number = {9},
pages = {094310},
publisher = {AIP Publishing},
abstract = {We present a model to study Young’s modulus and Poisson’s ratio of the composite material of amorphous nanowires. It is an extension of the model derived by two of us [da Fonseca and Galvão, Phys. Rev. Lett.92, 175502 (2004)] to study the elastic properties of amorphous nanosprings. The model is based on twisting and tensioning a straight nanowire and we propose an experimental setup to obtain the elastic parameters of the nanowire. We used the Kirchhoff rod model to obtain the expressions for the elastic constants of the nanowire.
},
keywords = {Elasticity, Filaments, Nanowires},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
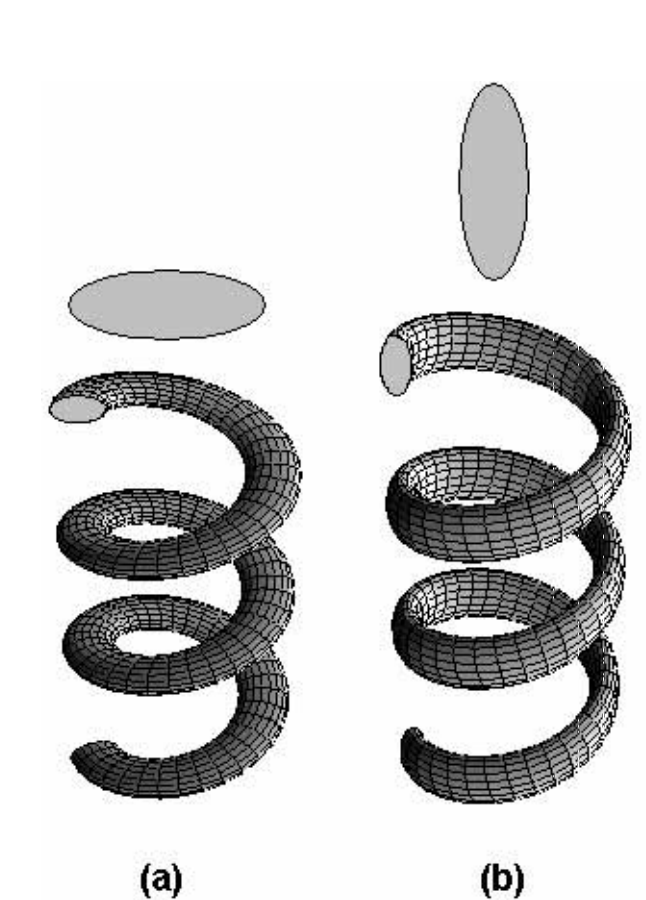
da Fonseca, Alexandre Fontes; Malta, CP; Galvao, Douglas S
Elastic Properties of Normal and Binormal Helical Nanowires Proceedings
Cambridge University Press, vol. 963, 2006.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Elasticity, Filaments, Metallic Nanowires
@proceedings{da2006elasticb,
title = {Elastic Properties of Normal and Binormal Helical Nanowires},
author = {da Fonseca, Alexandre Fontes and Malta, CP and Galvao, Douglas S},
url = {http://journals.cambridge.org/action/displayAbstract?fromPage=online&aid=8026852},
year = {2006},
date = {2006-01-01},
journal = {MRS Proceedings},
volume = {963},
pages = {0963--Q20},
publisher = {Cambridge University Press},
abstract = {A helical nanowire can be defined as being a nanoscopic rod whose axis follows a helical curve in space. In the case of a nanowire with asymmetric cross section, the helical nanostructure can be classified as normal or binormal helix, according to the orientation of the cross section with respect to the helical axis of the structure. In this work, we present a simple model to study the elastic properties of a helical nanowire with asymmetric cross section. We use the framework of the Kirchhoff rod model to obtain an expression relating the Hooke's constant, h, of normal and binormal nanohelices to their geometric features. We also obtain the Young's modulus values. These relations can be used by experimentalists to evaluate the elastic properties of helical nanostructures. We showed that the Hooke's constant of a normal nanohelix is higher than that of a binormal one. We illustrate our results using experimentally obtained nanohelices reported in the literature.},
keywords = {Elasticity, Filaments, Metallic Nanowires},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {proceedings}
}
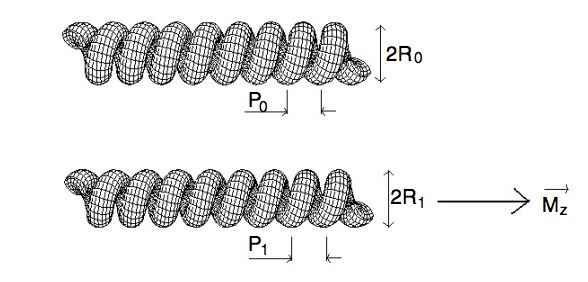
da Fonseca, Alexandre F; Malta, CP; Galvao, DS
Mechanical properties of amorphous nanosprings Journal Article
In: Nanotechnology, vol. 17, no. 22, pp. 5620, 2006.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Elasticity, Filaments, Nanowires
@article{da2006mechanical,
title = {Mechanical properties of amorphous nanosprings},
author = {da Fonseca, Alexandre F and Malta, CP and Galvao, DS},
url = {http://iopscience.iop.org/0957-4484/17/22/015},
year = {2006},
date = {2006-01-01},
journal = {Nanotechnology},
volume = {17},
number = {22},
pages = {5620},
publisher = {IOP Publishing},
abstract = {Helical amorphous nanosprings have attracted particular interest due to their special mechanical properties. In this work we present a simple model, within the framework of the Kirchhoff rod model, for investigating the structural properties of nanosprings having asymmetric cross section. We have derived expressions that can be used to obtain the Young's modulus and Poisson's ratio of the nanospring material composite. We also address the importance of the presence of a catalyst in the growth process of amorphous nanosprings in terms of the stability of helical rods.
},
keywords = {Elasticity, Filaments, Nanowires},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2005
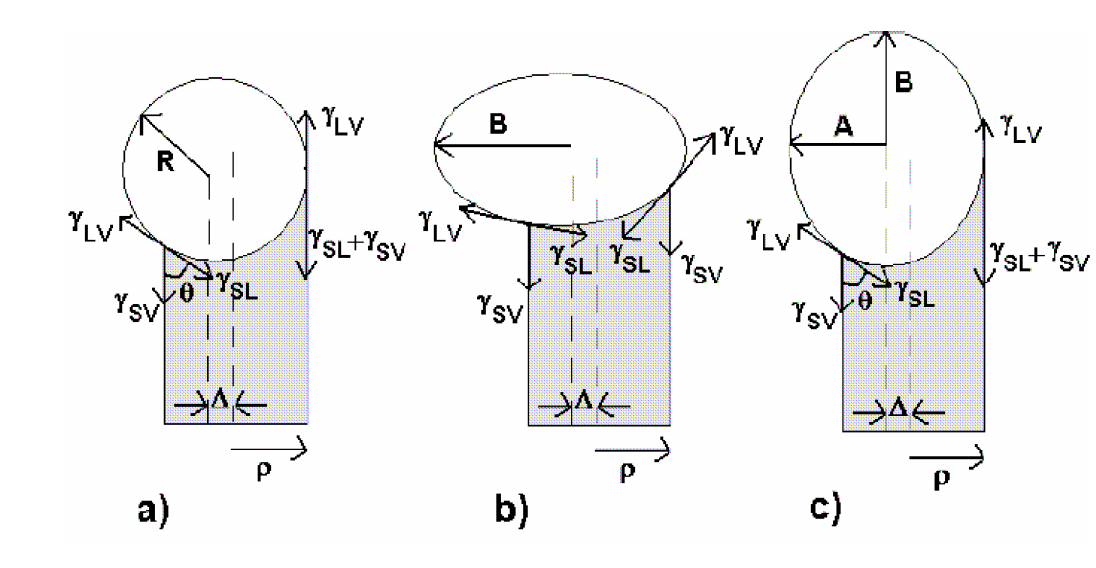
da Fonseca, Alexandre F; Galvao, Douglas S; Malta, Coraci P
Binormal nanohelices Proceedings
Cambridge University Press, vol. 903, 2005.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Elasticity, Filaments, Nanowires
@proceedings{da2005binormal,
title = {Binormal nanohelices},
author = {da Fonseca, Alexandre F and Galvao, Douglas S and Malta, Coraci P},
url = {http://journals.cambridge.org/action/displayAbstract?fromPage=online&aid=8108794&fileId=S1946427400047680},
year = {2005},
date = {2005-01-01},
journal = {MRS Proceedings},
volume = {903},
pages = {0903--Z14},
publisher = {Cambridge University Press},
abstract = {Helical structures can be classified in accordance with the orientation of its cross-section with respect to the normal or binormal vectors. We investigate the geometric features of several nanosprings verifying the non-existence of normal nanohelices. In this work, using the VLS growth model, we explain not only the absence of normal nanosprings but also the growing process of binormal nanosprings. The dynamical stability of crystalline ZnO binormal nanohelices is also addressed.},
keywords = {Elasticity, Filaments, Nanowires},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {proceedings}
}
2004
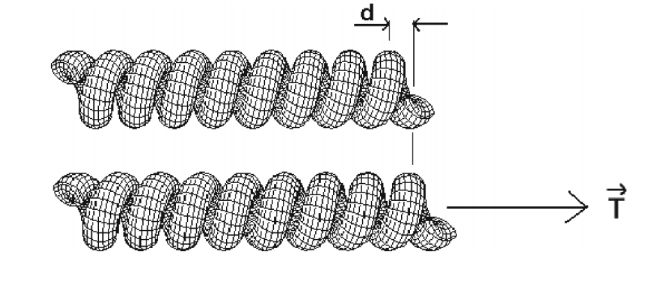
da Fonseca, Alexandre F; Galvao, Douglas S
Mechanical properties of nanosprings Journal Article
In: Physical review letters, vol. 92, no. 17, pp. 175502, 2004.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Elasticity, Filaments, Nanowires
@article{da2004mechanical,
title = {Mechanical properties of nanosprings},
author = {da Fonseca, Alexandre F and Galvao, Douglas S},
url = {http://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevLett.92.175502},
year = {2004},
date = {2004-01-01},
journal = {Physical review letters},
volume = {92},
number = {17},
pages = {175502},
publisher = {APS},
abstract = {Nanostructures (nanotubes, nanowires, etc.) have been the object of intense theoretical and experimental investigations in recent years. Among these structures, helical nanosprings or nanocoils have attracted particular interest due to their special mechanical properties. In this work, we investigated structural properties of nanosprings in the Kirchhoff rod model. We derived expressions that can be used experimentally to obtain nanospring Young’s modulus and Poisson’s ratio values. Our results also might explain why the presence of catalytic particles is so important in nanostructure growth.},
keywords = {Elasticity, Filaments, Nanowires},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
http://scholar.google.com/citations?hl=en&user=95SvbM8AAAAJ


